Bestatin attenuates breast cancer stemness by targeting puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase
- PMID: 38814491
- PMCID: PMC11139817
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01063-4
Bestatin attenuates breast cancer stemness by targeting puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase
Abstract
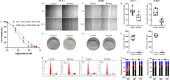
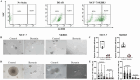
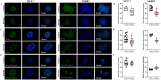
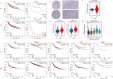
Breast cancer is a prevalent malignant tumor among women with an increasing incidence rate annually. Breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) are integral in impeding tumor advancement and addressing drug resistance. Bestatin serves as an adjuvant chemotherapy, triggering apoptosis in cancer cells. In this study, the effects of bestatin on sorted BCSCs from breast cancer cell lines have been studied. Our results indicated that bestatin inhibits the migration and proliferation of breast cancer cells by reducing the stemness of BCSCs both in vitro and in vivo. Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase is implicated in the process through the regulation of cell cycle, resulting in heightened cell apoptosis and diminished cell proliferation of BCSCs. Our study suggest that targeting cancer stem cell may offer a promising approach in breast cancer treatment, presenting noval therapeutic strategies for patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bestatin; Breast cancer; Breast cancer stem cells; Proliferation; Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
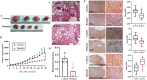
Figures
Similar articles
-
Augmentation of death ligand-induced apoptosis by aminopeptidase inhibitors in human solid tumor cell lines.Int J Cancer. 2001 Nov;94(4):485-91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.1492. Int J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11745433
-
Differentiation of breast cancer stem cells by knockdown of CD44: promising differentiation therapy.J Transl Med. 2011 Dec 7;9:209. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-209. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 22152097 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting Nanog inhibits cell proliferation and attenuates cancer stem cell activities in breast cancer.J Drug Target. 2016;24(5):422-32. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1082567. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Drug Target. 2016. PMID: 26339994
-
Role, molecular mechanism and the potential target of breast cancer stem cells in breast cancer development.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112616. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112616. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35008001 Review.
-
Breast Cancer Stem-Like Cells in Drug Resistance: A Review of Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 21;12:856974. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.856974. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35392236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artignan J, et al. Are breast cancer patients with suboptimal adherence to cardiovascular treatment more likely to discontinue adjuvant endocrine therapy? Competing risk survival analysis in a nationwide cohort of postmenopausal women. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03156-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
