The role of Matrin-3 in physiology and its dysregulation in disease
- PMID: 38813817
- PMCID: PMC11209761
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20220585
The role of Matrin-3 in physiology and its dysregulation in disease
Abstract
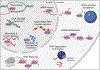
The dysfunction of many RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) that are heavily disordered, including TDP-43 and FUS, are implicated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (ALS/FTD). These proteins serve many important roles in the cell, and their capacity to form biomolecular condensates (BMCs) is key to their function, but also a vulnerability that can lead to misregulation and disease. Matrin-3 (MATR3) is an intrinsically disordered RBP implicated both genetically and pathologically in ALS/FTD, though it is relatively understudied as compared with TDP-43 and FUS. In addition to binding RNA, MATR3 also binds DNA and is implicated in many cellular processes including the DNA damage response, transcription, splicing, and cell differentiation. It is unclear if MATR3 localizes to BMCs under physiological conditions, which is brought further into question due to its lack of a prion-like domain. Here, we review recent studies regarding MATR3 and its roles in numerous physiological processes, as well as its implication in a range of diseases.
Keywords: Matrin-3; RNA-binding proteins; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; biomolecular condensates; intrinsically disordered proteins; neurodegeneration.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA dependent suppression of C9orf72 ALS/FTD associated neurodegeneration by Matrin-3.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Oct 31;8(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01060-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33129345 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Phase Separation and Amyloidosis of ALS/FTD-linked FUS and TDP-43.Aging Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(5):2084-2112. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1118. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38029395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains in health and disease.Biochem J. 2017 Apr 7;474(8):1417-1438. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160499. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28389532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TDP-43 and FUS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.Lancet Neurol. 2010 Oct;9(10):995-1007. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70195-2. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20864052 Review.
-
Post-translational modifications on RNA-binding proteins: accelerators, brakes, or passengers in neurodegeneration?Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Jan;47(1):6-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34366183 Review.
References
-
- Belgrader P, Dey R, Berezney R. Molecular cloning of matrin 3. A 125-kilodalton protein of the nuclear matrix contains an extensive acidic domain. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(15):9893–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

