PARP inhibitor synthetic lethality in ATM biallelic mutant cancer cell lines is associated with BRCA1/2 and RAD51 downregulation
- PMID: 38807759
- PMCID: PMC11131418
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1380633
PARP inhibitor synthetic lethality in ATM biallelic mutant cancer cell lines is associated with BRCA1/2 and RAD51 downregulation
Abstract
Background: Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) kinase is a central regulator of the DNA damage response (DDR) signaling pathway, and its function is critical for the maintenance of genomic stability in cells that coordinate a network of cellular processes, including DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell cycle progression. ATM is frequently mutated in human cancers, and approximately 3% of lung cancers have biallelic mutations in ATM, i.e., including 3.5% of lung adenocarcinomas (LUAD) and 1.4% of lung squamous cell carcinomas (LUSC).
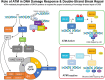
Methods: We investigated the potential of targeting the DDR pathway in lung cancer as a potential therapeutic approach. In this context, we examined whether ATM loss is synthetically lethal with niraparib monotherapy. This exploration involved the use of hATM knockout (KO) isogenic cell lines containing hATM homozygous (-/-) and heterozygous (+/-) generated via CRISPR/Cas9 gene knockout technology in DLD-1, a human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line. Subsequently, we extended our investigation to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient derived xenograft (PDX) models for further validation of poly ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitor (PARPi) synthetic lethality in ATM mutant NSCLC models.
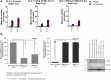
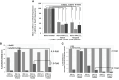
Results: Here, we demonstared that biallelic hATM deletion (-/-) in DLD-1 impairs homologous recombination (HR) repair function and sensitizes cells to the PARPi, niraparib. Niraparib also caused significant tumor regression in one-third of the NSCLC PDX models harboring deleterious biallelic ATM mutations. Loss of hATM (-/-) was concomitantly associated with low BRCA1 and BRCA2 protein expression in both the hATM (-/-) DLD-1 cell line and PARPi-sensitive ATM mutant NSCLC PDX models, suggesting a downstream effect on the impairment of HR-mediated DNA checkpoint signaling. Further analysis revealed that loss of ATM led to inhibition of phosphorylation of MRN (Mre11-Rad50-NBS1) complex proteins, which are required for ATM-mediated downstream phosphorylation of p53, BRCA1, and CHK2.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings highlight that the synthetic lethality of niraparib in ATM-deficient tumors can be regulated through a subsequent effect on the modulation of BRCA1/2 expression and its effect on HR function.
Keywords: ATM kinase; DNA double strand break (DSB) repair; PARP; genomic instability; homologous recombination deficiency; non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC); synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2024 Muvaffak and Coleman.
Conflict of interest statement
Both authors, AM and KC, are employees of and hold ownership interest in GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Defective Mre11-dependent activation of Chk2 by ataxia telangiectasia mutated in colorectal carcinoma cells in response to replication-dependent DNA double strand breaks.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 13;281(41):30814-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603747200. Epub 2006 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16905549
-
Productive replication of human papillomavirus 31 requires DNA repair factor Nbs1.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8528-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00517-14. Epub 2014 May 21. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24850735 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC8 mutation causes hypersensitivity to PARP inhibition without Homologous recombination repair deficiency.Mutat Res. 2023 Jan-Jun;826:111815. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2023.111815. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Mutat Res. 2023. PMID: 36812659
-
DNA-Damage-Repair Gene Alterations in Genitourinary Malignancies.Eur Surg Res. 2022;63(4):155-164. doi: 10.1159/000526415. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Eur Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35944490 Review.
-
An insight into understanding the coupling between homologous recombination mediated DNA repair and chromatin remodeling mechanisms in plant genome: an update.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1760-1784. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966584. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34437813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

