Integrating single-cell and multi-omic approaches reveals Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38801409
- PMCID: PMC11129731
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18317
Integrating single-cell and multi-omic approaches reveals Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction in non-small-cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'Integrating Single-Cell and Multi-Omic Approaches Reveals Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba-Dependent Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer'.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Dec;28(24):e70305. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70305. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39727254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
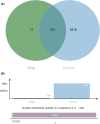
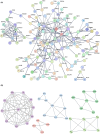
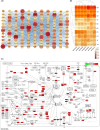
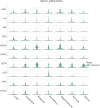
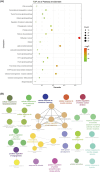
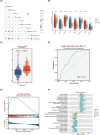
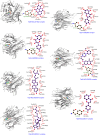
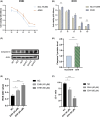
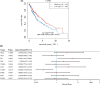
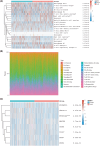
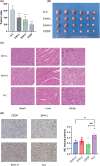
Euphorbiae Humifusae Herba (EHH) is a pivotal therapeutic agent with diverse pharmacological effects. However, a substantial gap exists in understanding its pharmacological properties and anti-tumour mechanisms. This study aimed to address this gap by exploring EHH's pharmacological properties, identifying NSCLC therapy-associated protein targets, and elucidating how EHH induces mitochondrial disruption in NSCLC cells, offering insights into novel NSCLC treatment strategies. String database was utilized to explore protein-protein interactions. Subsequently, single-cell analysis and multi-omics further unveiled the impact of EHH-targeted genes on the immune microenvironment of NSCLC, as well as their influence on immunotherapeutic responses. Finally, both in vivo and in vitro experiments elucidated the anti-tumour mechanisms of EHH, specifically through the assessment of mitochondrial ROS levels and alterations in mitochondrial membrane potential. EHH exerts its influence through engagement with a cluster of 10 genes, including the apoptotic gene CASP3. This regulatory impact on the immune milieu within NSCLC holds promise as an indicator for predicting responses to immunotherapy. Besides, EHH demonstrated the capability to induce mitochondrial ROS generation and perturbations in mitochondrial membrane potential in NSCLC cells, ultimately leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and consequent apoptosis of tumour cells. EHH induces mitochondrial disruption in NSCLC cells, leading to cell apoptosis to inhibit the progress of NSCLC.
Keywords: EHH; NSCLC; immune; mitochondrial dysfunction; multi‐omics; single‐cell.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the Mechanism of Ferroptosis Induction by Sappanone A in Cancer: Insights into the Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated by NRF2/xCT/GPX4 Axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;20(13):5145-5161. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.96748. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39430236 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-cancer effect of sodium pentaborate in combination with cisplatin on lung cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 29;52(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10119-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39612011
-
Identification of a novel toxicophore in anti-cancer chemotherapeutics that targets mitochondrial respiratory complex I.Elife. 2020 May 20;9:e55845. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55845. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32432547 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Cellular dynamics of tumor microenvironment driving immunotherapy resistance in non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2024 Nov 1;604:217272. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217272. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 39326553 Review.
References
-
- Gong X, Chi H, Xia Z, Yang G, Tian G. Advances in HPV‐associated tumor management: therapeutic strategies and emerging insights. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28950. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20Y21902300/Shanghai Medical Innovation Research Project of "Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan"
- 2022YQ028/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, Health Youth Talent Project
- SHDC2020CR4050/Shanghai Hospital Development Center
- YM2021023/LongHua Hospital Medical Scholars Scheme
- SHDC12020123/Shanghai Municipal Hospital Development Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

