Effector function and neutrophil cell death in the severity of sepsis with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38798871
- PMCID: PMC11125301
- DOI: 10.52225/narra.v4i1.532
Effector function and neutrophil cell death in the severity of sepsis with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
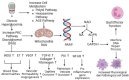
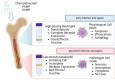
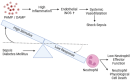
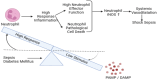
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from immune dysregulation, is typically triggered by bacterial infections and commonly coexists with diabetes mellitus. Neutrophils are the first responders to infection and require regulated activation to control pathogen and damage-associated molecular patterns. Dysregulation of neutrophil activation leads to uncontrolled inflammatory responses, often observed in both sepsis and diabetes patients. Neutrophil dysregulation, characterized by effector dysfunction and inadequate cell death processes, can serve as a biomarker for assessing sepsis severity, particularly in diabetic patients. This review provides information on the relationship between effector function, neutrophil cell death, and the severity of sepsis in individuals with diabetes mellitus, aiming to shed light on the mechanisms underlying sepsis progression. Topics covered in the review include an overview of effector function of neutrophil cells, mechanisms of neutrophil cell death, and dysregulation of effectors and neutrophil cell death processes in sepsis severity with diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Sepsis; cell death; diabetes; effector function; neutrophil.
© 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil dysregulation during sepsis: an overview and update.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Sep;21(9):1687-1697. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13112. Epub 2017 Feb 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28244690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic roles of neutrophil in bloodstream infections.Immunobiology. 2020 Jan;225(1):151858. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2019.10.007. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Immunobiology. 2020. PMID: 31836303 Review.
-
Glucagon Reduces Neutrophil Migration and Increases Susceptibility to Sepsis in Diabetic Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 6;12:633540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.633540. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34295325 Free PMC article.
-
Complement 5a receptor-mediated neutrophil dysfunction is associated with a poor outcome in sepsis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;13(1):103-9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.136. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 25726869 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of neutrophil death in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 18;13:963955. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.963955. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A retrospective study utilized MIMIC-IV database to explore the potential association between triglyceride-glucose index and mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 15;14(1):24081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75050-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Purba AKR, Mariana N, Aliska G, et al. . The burden and costs of sepsis and reimbursement of its treatment in a developing country: An observational study on focal infections in Indonesia. Int J Infect Dis 2020;96:211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
