Transcriptional Control of Seed Life: New Insights into the Role of the NAC Family
- PMID: 38791407
- PMCID: PMC11121595
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105369
Transcriptional Control of Seed Life: New Insights into the Role of the NAC Family
Abstract
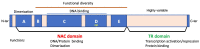
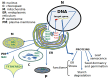
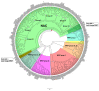
Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences on DNA through their DNA-binding domain (DBD), a universal process. This update conveys information about the diverse roles of TFs, focusing on the NACs (NAM-ATAF-CUC), in regulating target-gene expression and influencing various aspects of plant biology. NAC TFs appeared before the emergence of land plants. The NAC family constitutes a diverse group of plant-specific TFs found in mosses, conifers, monocots, and eudicots. This update discusses the evolutionary origins of plant NAC genes/proteins from green algae to their crucial roles in plant development and stress response across various plant species. From mosses and lycophytes to various angiosperms, the number of NAC proteins increases significantly, suggesting a gradual evolution from basal streptophytic green algae. NAC TFs play a critical role in enhancing abiotic stress tolerance, with their function conserved in angiosperms. Furthermore, the modular organization of NACs, their dimeric function, and their localization within cellular compartments contribute to their functional versatility and complexity. While most NAC TFs are nuclear-localized and active, a subset is found in other cellular compartments, indicating inactive forms until specific cues trigger their translocation to the nucleus. Additionally, it highlights their involvement in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced programmed cell death (PCD) by activating the vacuolar processing enzyme (VPE) gene. Moreover, this update provides a comprehensive overview of the diverse roles of NAC TFs in plants, including their participation in ER stress responses, leaf senescence (LS), and growth and development. Notably, NACs exhibit correlations with various phytohormones (i.e., ABA, GAs, CK, IAA, JA, and SA), and several NAC genes are inducible by them, influencing a broad spectrum of biological processes. The study of the spatiotemporal expression patterns provides insights into when and where specific NAC genes are active, shedding light on their metabolic contributions. Likewise, this review emphasizes the significance of NAC TFs in transcriptional modules, seed reserve accumulation, and regulation of seed dormancy and germination. Overall, it effectively communicates the intricate and essential functions of NAC TFs in plant biology. Finally, from an evolutionary standpoint, a phylogenetic analysis suggests that it is highly probable that the WRKY family is evolutionarily older than the NAC family.
Keywords: TF binding sites; WRKY and NAC families; endoplasmic reticulum; endosperm; phytohormones; seed dormancy and germination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Discarded sequencing reads uncover natural variation in pest resistance in Thlaspi arvense.Elife. 2024 Dec 19;13:RP95510. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95510. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39699583 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of school-based family asthma educational programs on the quality of life and number of asthma exacerbations of children aged five to 18 years diagnosed with asthma: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):69-81. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2335. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571284
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Child, family and professional views on valued communication outcomes for non-verbal children with neurodisability: A qualitative meta-synthesis.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024 Nov-Dec;59(6):2946-2984. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.13121. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 39417318 Review.
References
-
- Chowdhary A.A., Mishra S., Mehrotra S., Upadhyay S.K., Bagal D., Srivastava V. Plant transcription factors: An overview of their role in plant life. Plant Transcr. Factors. 2023:3–20. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-90613-5.00003-0. - DOI
-
- Rui Z., Pan W., Zhao Q., Hu H., Li X., Xing L., Jia H., She K., Nie X. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of NAC gene family under salt stress in wild emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccoides L.) Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;230:12337. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123376. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

