About a Possible Impact of Endodontic Infections by Fusobacterium nucleatum or Porphyromonas gingivalis on Oral Carcinogenesis: A Literature Overview
- PMID: 38791123
- PMCID: PMC11121237
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25105083
About a Possible Impact of Endodontic Infections by Fusobacterium nucleatum or Porphyromonas gingivalis on Oral Carcinogenesis: A Literature Overview
Abstract
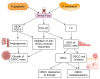
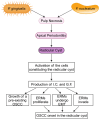
Periodontitis is linked to the onset and progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), an epidemiologically frequent and clinically aggressive malignancy. In this context, Fusobacterium (F.) nucleatum and Porphyromonas (P.) gingivalis, two bacteria that cause periodontitis, are found in OSCC tissues as well as in oral premalignant lesions, where they exert pro-tumorigenic activities. Since the two bacteria are present also in endodontic diseases, playing a role in their pathogenesis, here we analyze the literature searching for information on the impact that endodontic infection by P. gingivalis or F. nucleatum could have on cellular and molecular events involved in oral carcinogenesis. Results from the reviewed papers indicate that infection by P. gingivalis and/or F. nucleatum triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in dental pulp cells or periodontal cells, affecting the survival, proliferation, invasion, and differentiation of OSCC cells. In addition, the two bacteria and the cytokines they induce halt the differentiation and stimulate the proliferation and invasion of stem cells populating the dental pulp or the periodontium. Although most of the literature confutes the possibility that bacteria-induced endodontic inflammatory diseases could impact on oral carcinogenesis, the papers we have analyzed and discussed herein recommend further investigations on this topic.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; Porphyromonas gingivalis; endodontic infections; endodontic neoplasms; odontogenic tumors; oral premalignant diseases; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periodontal pathogens Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum promote tumor progression in an oral-specific chemical carcinogenesis model.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 8;6(26):22613-23. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4209. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26158901 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Pathways Triggered by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum: Therapeutic Possibilities?Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Jun 24;2019:7241312. doi: 10.1155/2019/7241312. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31341421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of coaggregation between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum on the host response to mixed infection.J Clin Periodontol. 2012 Jul;39(7):617-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01889.x. Epub 2012 May 21. J Clin Periodontol. 2012. PMID: 22607053
-
Mouse model of experimental periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis/Fusobacterium nucleatum infection: bone loss and host response.J Clin Periodontol. 2009 May;36(5):406-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01393.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 19419440
-
Fusobacterium nucleatum and oral cancer: a critical review.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 13;21(1):1212. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08903-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34774023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Oral Microbiome Dysbiosis on the Aetiology, Pathogenesis, and Development of Oral Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;16(17):2997. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172997. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers Identification in the Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review of Proteomic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 16;25(16):8929. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168929. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201614 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Angiogenic Factors on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Their Impact on the Onset and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1294. doi: 10.3390/cells13151294. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

