Identification of Biotransformation Products of T-2 Toxin in HepG2 Cells Using LC-Q-TOF MS
- PMID: 38790801
- PMCID: PMC11120489
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13101501
Identification of Biotransformation Products of T-2 Toxin in HepG2 Cells Using LC-Q-TOF MS
Abstract
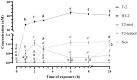
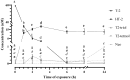
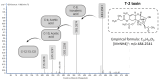
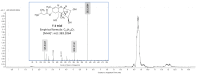
The T-2 toxin (T-2) is a type A trichothecene found in cereals. The formation of metabolites is a frequent cause of mycotoxin-induced toxicity. In this work, the conversion of T-2 during biotransformation reactions in HepG2 cells was evaluated. For this, HepG2 cells were exposed to 30 (IC50/2) and 60 (IC50) nM of T-2 for 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 8 and 24 h, and the concentrations of T-2 and its metabolites HT-2, T2-triol, T2-tetraol and neosolaniol were determined in both the cell fraction and culture medium through liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry-time of flight (LC-Q-TOF MS). Results showed a fast metabolization of T-2 (>90%) during the first 2 h, with HT-2 as its main (>95%) biotransformation product. The cell fraction showed higher levels (p < 0.05) of HT-2 (39.9 ± 2.1 nM) compared to the culture medium (12.53 ± 2.4 nM). This trend was also observed for the identified metabolites. T2-triol reached its maximum concentration (1.7 ± 0.4 nM) at 2 h, and at later times a time-dependent increase in the T2-tetraol and neosolaniol concentrations was observed. The identification of T-2 metabolites shows the need to continue combined toxicity studies of mycotoxins for a correct risk characterization of these natural contaminants.
Keywords: HepG2; LC-Q-TOF MS; T-2; biotransformation; in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
T-2 toxin and its metabolites: Characterization, cytotoxic mechanisms and adaptive cellular response in human hepatocarcinoma (HepG2) cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Nov;145:111654. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111654. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32777337
-
Determination of T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, and three other type A trichothecenes in layer feed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)--comparison of two sample preparation methods.Mycotoxin Res. 2016 May;32(2):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s12550-016-0244-z. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Mycotoxin Res. 2016. PMID: 26940912
-
Interactions between T-2 toxin and its metabolites in HepG2 cells and in silico approach.Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Feb;148:111942. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111942. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33359025
-
Metabolic pathways of trichothecenes.Drug Metab Rev. 2010 May;42(2):250-67. doi: 10.1080/03602530903125807. Drug Metab Rev. 2010. PMID: 19678805 Review.
-
Metabolic pathways of T-2 toxin.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 Jan;9(1):77-82. doi: 10.2174/138920008783331176. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18220574 Review.
References
-
- Chen P., Xiang B., Shi H., Yu P., Song Y., Li S. Recent Advances on Type A Trichothecenes in Food and Feed: Analysis, Prevalence, Toxicity, and Decontamination Techniques. Food Control. 2020;118:107371. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107371. - DOI
-
- Food Balance Sheet, 20 March 2020. FAOSTAT. [(accessed on 4 April 2024)]. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

