Tert-Butylhydroquinone Mitigates T-2-Toxin-Induced Testicular Dysfunction by Targeting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats
- PMID: 38787114
- PMCID: PMC11125982
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12050335
Tert-Butylhydroquinone Mitigates T-2-Toxin-Induced Testicular Dysfunction by Targeting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats
Abstract
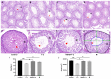
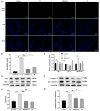
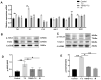
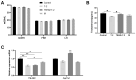
Tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) has emerged as a promising candidate for mitigating the adverse effects of T-2-induced reproductive toxicity. The protective effects of tBHQ on rat sperm quality, testicular injury, apoptosis, and inflammation induced by T-2 toxin exposure were investigated. Histopathological examination of testicular tissues revealed severe damage in the T-2-treated group, characterized by disorganized germ cell arrangement, thinning of the convoluted seminiferous tubule walls, and significant cellular necrosis. However, tBHQ administration, either as a preventive or therapeutic measure, mitigated this structural damage. Image analysis confirmed an increase in the cross-sectional area and height of the convoluted seminiferous tubules in the tBHQ-treated groups compared to the T-2-treated group (p < 0.05), indicating tBHQ's efficacy in alleviating testicular damage. Additionally, tBHQ treatment significantly inhibited T-2-induced apoptosis of testicular tissue cells, as evidenced by the results showing reduced apoptotic cell counts and downregulation of the BAX/BCL2 ratio and caspase-3 expression (p < 0.05). tBHQ significantly increased the concentrations of the antioxidant factors SOD, CAT, TAC, and GSH-PX. Furthermore, tBHQ attenuated the inflammatory response induced by T-2 exposure, as indicated by the decreased mRNA expression of the proinflammatory cytokines Tnf, Il1, and Il10 in testicular tissue (p < 0.05). Additionally, tBHQ treatment alleviated the decline in serum testosterone induced by the T-2 and promoted testosterone synthesis gene expression, including for the genes 17β-HSD and Cyp11a1, in rat testes (p < 0.05). These findings underscore tBHQ's role as a therapeutic agent combatting T-2-induced reproductive toxicity, highlighting its antioxidative, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Further elucidation of tBHQ's mechanisms of action may offer novel strategies for preventing and treating reproductive disorders induced by environmental toxins.
Keywords: T-2; apoptosis; inflammation; oxidative stress; tert-butylhydroquinone; testis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone preserve testicular steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in cisplatin-intoxicated rats by targeting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.Toxicology. 2020 Aug;441:152528. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2020.152528. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Toxicology. 2020. PMID: 32565124
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone attenuates scrotal heat-induced damage by regulating Nrf2-antioxidant system in the mouse testis.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Nov 1;208:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.09.007. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25260249
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone protects PC12 cells against ferrous sulfate-induced oxidative and inflammatory injury via the Nrf2/ARE pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2017 Aug 1;273:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.05.021. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2017. PMID: 28583816
-
tert-Butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) protects hepatocytes against lipotoxicity via inducing autophagy independently of Nrf2 activation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1841(1):22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24055888 Free PMC article.
-
Alarming impact of the excessive use of tert-butylhydroquinone in food products: A narrative review.Toxicol Rep. 2022 May 2;9:1066-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.04.027. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- 2023A1515010232/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 99000639/Scientific Research Foundation of Shaoguan University for the Introduction of Talents
- 32272873/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022KJ126/Project of Swine Innovation Team in Guangdong Modern Agricultural Research System
- Sycxcy2023087/School-level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

