BSA Binding and Aggregate Formation of a Synthetic Amino Acid with Potential for Promoting Fibroblast Proliferation: An In Silico, CD Spectroscopic, DLS, and Cellular Study
- PMID: 38785986
- PMCID: PMC11118884
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14050579
BSA Binding and Aggregate Formation of a Synthetic Amino Acid with Potential for Promoting Fibroblast Proliferation: An In Silico, CD Spectroscopic, DLS, and Cellular Study
Abstract
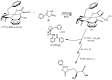
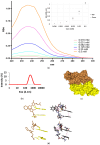
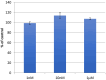
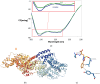
This study presents the chemical synthesis, purification, and characterization of a novel non-natural synthetic amino acid. The compound was synthesized in solution, purified, and characterized using NMR spectroscopy, polarimetry, and melting point determination. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) analysis demonstrated its ability to form aggregates with an average size of 391 nm, extending to the low micrometric size range. Furthermore, cellular biological assays revealed its ability to enhance fibroblast cell growth, highlighting its potential for tissue regenerative applications. Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy showed the ability of the synthetic amino acid to bind serum albumins (using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a model), and CD deconvolution provided insights into the changes in the secondary structures of BSA upon interaction with the amino acid ligand. Additionally, molecular docking using HDOCK software elucidated the most likely binding mode of the ligand inside the BSA structure. We also performed in silico oligomerization of the synthetic compound in order to obtain a model of aggregate to investigate computationally. In more detail, the dimer formation achieved by molecular self-docking showed two distinct poses, corresponding to the lowest and comparable energies, with one pose exhibiting a quasi-coplanar arrangement characterized by a close alignment of two aromatic rings from the synthetic amino acids within the dimer, suggesting the presence of π-π stacking interactions. In contrast, the second pose displayed a non-coplanar configuration, with the aromatic rings oriented in a staggered arrangement, indicating distinct modes of interaction. Both poses were further utilized in the self-docking procedure. Notably, iterative molecular docking of amino acid structures resulted in the formation of higher-order aggregates, with a model of a 512-mer aggregate obtained through self-docking procedures. This model of aggregate presented a cavity capable of hosting therapeutic cargoes and biomolecules, rendering it a potential scaffold for cell adhesion and growth in tissue regenerative applications. Overall, our findings highlight the potential of this synthetic amino acid for tissue regenerative therapeutics and provide valuable insights into its molecular interactions and aggregation behavior.
Keywords: fibroblast growth enhancement; in silico; protein binding; self-assembling system; synthetic amino acid; tissue regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein Binding of Benzofuran Derivatives: A CD Spectroscopic and In Silico Comparative Study of the Effects of 4-Nitrophenyl Functionalized Benzofurans and Benzodifurans on BSA Protein Structure.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 5;12(2):262. doi: 10.3390/biom12020262. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204762 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the binding interaction of quinoline yellow with bovine serum albumin and anti-amyloidogenic behavior of ferulic acid on QY-induced BSA fibrils.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 May 15;313:124076. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2024.124076. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024. PMID: 38442614
-
How does cholinium cation surpass tetraethylammonium cation in amino acid-based ionic liquids for thermal and structural stability of serum albumins?Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Apr 1;148:615-626. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.135. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31954128
-
CD, UV, and In Silico Insights on the Effect of 1,3-Bis(1'-uracilyl)-2-propanone on Serum Albumin Structure.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 3;12(8):1071. doi: 10.3390/biom12081071. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36008965 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic study on the interaction between mononaphthalimide spermidine (MINS) and bovine serum albumin (BSA).J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015 Jan;142:103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Dec 6. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015. PMID: 25528194
Cited by
-
In Silico Exploration of Novel EGFR Kinase Mutant-Selective Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Computational Approach.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;17(9):1107. doi: 10.3390/ph17091107. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scognamiglio P.L., Riccardi C., Palumbo R., Gale T.F., Musumeci D., Roviello G.N. Self-assembly of thyminyl l-tryptophanamide (TrpT) building blocks for the potential development of drug delivery nanosystems. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2023:1–19. doi: 10.1007/s40097-023-00523-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

