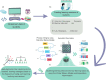
Providing insights into health data science education through artificial intelligence
- PMID: 38783229
- PMCID: PMC11118569
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-05555-3
Providing insights into health data science education through artificial intelligence
Abstract
Background: Health Data Science (HDS) is a novel interdisciplinary field that integrates biological, clinical, and computational sciences with the aim of analysing clinical and biological data through the utilisation of computational methods. Training healthcare specialists who are knowledgeable in both health and data sciences is highly required, important, and challenging. Therefore, it is essential to analyse students' learning experiences through artificial intelligence techniques in order to provide both teachers and learners with insights about effective learning strategies and to improve existing HDS course designs.
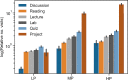
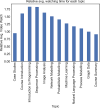
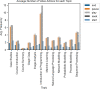
Methods: We applied artificial intelligence methods to uncover learning tactics and strategies employed by students in an HDS massive open online course with over 3,000 students enrolled. We also used statistical tests to explore students' engagement with different resources (such as reading materials and lecture videos) and their level of engagement with various HDS topics.
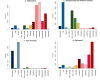
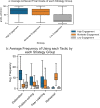
Results: We found that students in HDS employed four learning tactics, such as actively connecting new information to their prior knowledge, taking assessments and practising programming to evaluate their understanding, collaborating with their classmates, and repeating information to memorise. Based on the employed tactics, we also found three types of learning strategies, including low engagement (Surface learners), moderate engagement (Strategic learners), and high engagement (Deep learners), which are in line with well-known educational theories. The results indicate that successful students allocate more time to practical topics, such as projects and discussions, make connections among concepts, and employ peer learning.
Conclusions: We applied artificial intelligence techniques to provide new insights into HDS education. Based on the findings, we provide pedagogical suggestions not only for course designers but also for teachers and learners that have the potential to improve the learning experience of HDS students.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Educational data mining; Health data science; Health informatics; Learning analytics; Learning engagement; Learning strategy; Learning tactic; Medical education.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying Learning Preferences and Strategies in Health Data Science Courses: Systematic Review.JMIR Med Educ. 2024 Aug 12;10:e50667. doi: 10.2196/50667. JMIR Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39133909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI Education for Fourth-Year Medical Students: Two-Year Experience of a Web-Based, Self-Guided Curriculum and Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Med Educ. 2024 Feb 20;10:e46500. doi: 10.2196/46500. JMIR Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38376896 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Students' Professional Development as Educators Revealed Through Reflections on Their Teaching Following a Students-as-Teachers Course.Teach Learn Med. 2017 Oct-Dec;29(4):411-419. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2017.1302801. Epub 2017 May 12. Teach Learn Med. 2017. PMID: 28497991
-
Self-Reported Learning Strategies and Preferences in Health Informatics.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024 Aug 22;316:1540-1544. doi: 10.3233/SHTI240710. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024. PMID: 39176499
-
When learners become teachers: a review of peer teaching in medical student education.Fam Med. 2014 Nov-Dec;46(10):783-7. Fam Med. 2014. PMID: 25646829 Review.
References
-
- Muni Kumar N, Manjula R. Role of big data analytics in rural health care-A step towards svasth bharath. Int J Comput Sci Inform Technol. 2014;5(6):7172–8.
-
- Burghard C. Big data and analytics key to accountable care success. IDC Health Insights. 2012;1:1–9.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

