Rictor/mTORC2 signalling contributes to renal vascular endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal allograft interstitial fibrosis by regulating BNIP3-mediated mitophagy
- PMID: 38769658
- PMCID: PMC11106512
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.1686
Rictor/mTORC2 signalling contributes to renal vascular endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal allograft interstitial fibrosis by regulating BNIP3-mediated mitophagy
Abstract
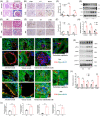
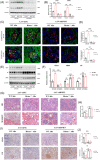
Background: Renal allograft interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy (IF/TA) constitutes the principal histopathological characteristic of chronic allograft dysfunction (CAD) in kidney-transplanted patients. While renal vascular endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) has been verified as an important contributing factor to IF/TA in CAD patients, its underlying mechanisms remain obscure. Through single-cell transcriptomic analysis, we identified Rictor as a potential pivotal mediator for EndMT. This investigation sought to elucidate the role of Rictor/mTORC2 signalling in the pathogenesis of renal allograft interstitial fibrosis and the associated mechanisms.
Methods: The influence of the Rictor/mTOR2 pathway on renal vascular EndMT and renal allograft fibrosis was investigated by cell experiments and Rictor depletion in renal allogeneic transplantation mice models. Subsequently, a series of assays were conducted to explore the underlying mechanisms of the enhanced mitophagy and the ameliorated EndMT resulting from Rictor knockout.
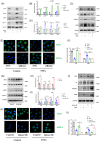
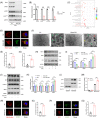
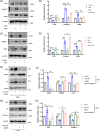
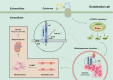
Results: Our findings revealed a significant activation of the Rictor/mTORC2 signalling in CAD patients and allogeneic kidney transplanted mice. The suppression of Rictor/mTORC2 signalling alleviated TNFα-induced EndMT in HUVECs. Moreover, Rictor knockout in endothelial cells remarkably ameliorated renal vascular EndMT and allograft interstitial fibrosis in allogeneic kidney transplanted mice. Mechanistically, Rictor knockout resulted in an augmented BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in endothelial cells. Furthermore, Rictor/mTORC2 facilitated the MARCH5-mediated degradation of BNIP3 at the K130 site through K48-linked ubiquitination, thereby regulating mitophagy activity. Subsequent experiments also demonstrated that BNIP3 knockdown nearly reversed the enhanced mitophagy and mitigated EndMT and allograft interstitial fibrosis induced by Rictor knockout.
Conclusions: Consequently, our study underscores Rictor/mTORC2 signalling as a critical mediator of renal vascular EndMT and allograft interstitial fibrosis progression, exerting its impact through regulating BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. This insight unveils a potential therapeutic target for mitigating renal allograft interstitial fibrosis.
Keywords: Rictor/mTORC2; mitophagy; renal allograft interstitial fibrosis; vascular endothelial cells.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Src inhibition modulates AMBRA1-mediated mitophagy to counteract endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal allograft fibrosis.Cell Prolif. 2024 Nov;57(11):e13699. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13699. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38943534 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired ATG16L-Dependent Autophagy Promotes Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in Chronic Renal Graft Dysfunction Through Inducing EndMT by NF-κB Signal Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 13;12:650424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650424. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33927720 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 promotes macrophage activation and kidney fibrosis.J Pathol. 2017 Aug;242(4):488-499. doi: 10.1002/path.4921. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28585302
-
Role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β1 in transplant kidney interstitial fibrosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Oct;21(10):2359-2369. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13157. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28374926 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking the impact of Rictor in cancer: novel insights of mTORC2 complex.Carcinogenesis. 2018 Jul 30;39(8):971-980. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy086. Carcinogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29955840 Review.
References
-
- Voora S, Adey DB. Management of kidney transplant recipients by general nephrologists: core Curriculum 2019. Am J Kidney Dis.. 2019;73(6):866‐879. - PubMed
-
- Yang C, Qi R, Yang B. Pathogenesis of chronic allograft dysfunction progress to renal fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:101‐116. - PubMed
-
- Granata S, Benedetti C, Gambaro G, et al. Kidney allograft fibrosis: what we learned from latest translational research studies. J Nephrol. 2020;33(6):1201‐1211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
