SAP deletion promotes malignant insulinoma progression by inducing CXCL12 secretion from CAFs via the CXCR4/p38/ERK signalling pathway
- PMID: 38766687
- PMCID: PMC11103456
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18397
SAP deletion promotes malignant insulinoma progression by inducing CXCL12 secretion from CAFs via the CXCR4/p38/ERK signalling pathway
Abstract
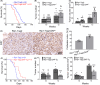
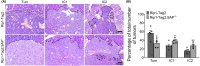
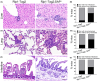
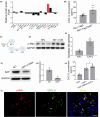
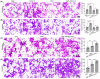
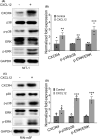
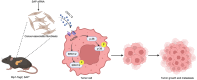
Malignant insulinoma is an extremely rare type of functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour with a high degree of malignancy and a high incidence of metastasis. However, it is still unclear how malignant insulinomas develop and metastasize. Serum amyloid P component (SAP), a member of the pentraxin protein family, is an acute-phase protein secreted by liver cells. The role of SAP in insulinoma and the related mechanism are still unknown. To determine the effect of SAP on insulinoma, we crossed Rip1-Tag2 mice, which spontaneously develop insulinoma, and SAP knockout (KO) mice to generate Rip1-Tag2;SAP-/- mice. We found that SAP deletion significantly promoted the growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant insulinoma through C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Further study showed that SAP deletion promoted CXCL12 secretion by CAFs through the CXCR4/p38/ERK signalling pathway. These findings reveal a novel role and mechanism of SAP in malignant insulinoma and provide direct evidence that SAP may be a therapeutic agent for this disease.
Keywords: CAF; CXCL12; SAP; insulinoma growth; insulinoma metastasis; malignant insulinoma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SDF-1α upregulation of MMP-2 is mediated by p38 MAPK signaling in pancreatic cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jul;40(7):4139-46. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2225-4. Epub 2013 May 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23712777
-
Stromal-derived factor-1α/CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic pathway promotes perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 10;6(7):4717-32. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3069. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25605248 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote progression and gemcitabine resistance via the SDF-1/SATB-1 pathway in pancreatic cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 18;9(11):1065. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1104-x. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30337520 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling axis in pancreatic cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(17):3371-4. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 24033967 Review.
-
The chemokine receptors CXCR4/CXCR7 and their primary heterodimeric ligands CXCL12 and CXCL12/high mobility group box 1 in pancreatic cancer growth and development: finding flow.Pancreas. 2015 May;44(4):528-34. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000298. Pancreas. 2015. PMID: 25872129 Review.
References
-
- Pelengaris S, Khan M. Oncogenic co‐operation in β‐cell tumorigenesis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001;8(4):307‐314. - PubMed
-
- Oberg K, Eriksson B. Endocrine tumours of the pancreas. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;19(5):753‐781. - PubMed
-
- Xi D, Luo T, Xiong H, et al. SAP: structure, function, and its roles in immune‐related diseases. Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:20‐26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

