Preliminary Exploration of Potential Active Ingredients and Molecular Mechanisms of Yanggan Yishui Granules for Treating Hypertensive Nephropathy Using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Coupled with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Strategy
- PMID: 38766523
- PMCID: PMC11101260
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/7967999
Preliminary Exploration of Potential Active Ingredients and Molecular Mechanisms of Yanggan Yishui Granules for Treating Hypertensive Nephropathy Using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Coupled with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Strategy
Abstract
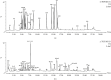
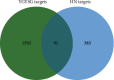
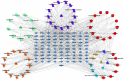
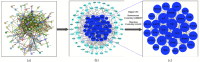
Hypertensive nephropathy (HN) is a prevalent complication of hypertension and stands as the second primary reason for end-stage renal disease. Research in clinical settings has revealed that Yanggan Yishui Granule (YGYSG) has significant therapeutic effects on HN. However, the material basis and action mechanisms of YGYSG against HN remain unclear. Consequently, this study utilized a comprehensive method integrating ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF/MS), network pharmacology, and molecular docking to delineate the active ingredients and potential therapeutic mechanisms of YGYSG for treating HN. Firstly, sixty distinct components were recognized in total as potential active ingredients in YGYSG by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Subsequently, the mechanisms of YGYSG against HN were revealed for the first time using network pharmacology. 23 ingredients played key roles in the complete network and were the key active ingredients, which could affect the renin-angiotensin system, fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, HIF-1 signaling pathway, and AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications by regulating 29 key targets such as TNF, IL6, ALB, EGFR, ACE, and MMP2. YGYSG could treat HN through the suppression of inflammatory response and oxidative stress, attenuating the proliferation of renal vascular smooth muscle cells, lessening glomerular capillary systolic pressure, and ameliorating renal dysfunction and vascular damage through the aforementioned targets and pathways. Molecular docking results revealed that most key active ingredients exhibited a high affinity for binding to the key targets. This study pioneers in clarifying the bioactive compounds and molecular mechanisms of YGYSG against HN and offers scientific reference into the clinical application.
Copyright © 2024 Fan Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An integrated strategy of UPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis, network pharmacology, and molecular docking to explore the chemical constituents and mechanism of Zixue Powder against febrile seizures.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 15;10(1):e23865. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23865. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38192830 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the pharmacological mechanisms of Biyan Qingdu Granula in the treatment after nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy based on UPLC/Q-TOF MS, network pharmacology and molecular docking.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Feb 15;239:115830. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115830. Epub 2023 Oct 30. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38096633
-
Integrating network pharmacology, UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and molecular docking to investigate the effect and mechanism of Chuanxiong Renshen decoction against Alzheimer's disease.Chin Med. 2022 Dec 24;17(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00698-1. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36566207 Free PMC article.
-
A breakthrough in periodontitis treatment: Revealing the pharmacodynamic substances and mechanisms of Kouqiangjie formula.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 6;323:117738. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117738. Epub 2024 Jan 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38199336
-
The active ingredients and mechanisms of Longchai Jiangxue Formula in treating PV, based on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS, systematic pharmacology, and molecular biology validation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Aug;140:111767. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111767. Epub 2021 May 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34058439
References
-
- Xie T., Bai Z. Y., Chen Z. D., et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis ameliorates hypertensive nephropathy through p53/Nrf2/p21 pathway by Taohongsiwu decoction: based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Journal of Ethnopharmacology . 2023;312 doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116506. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
