An automatic measurement method for the response of Caenorhabditis elegans to chemicals
- PMID: 38759045
- PMCID: PMC11191428
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-248013
An automatic measurement method for the response of Caenorhabditis elegans to chemicals
Abstract
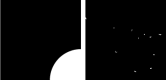
Background: Caenorhabditis elegans is a widely used model animal. Chemotaxis assay is one of the experiments that study the effects of different chemicals on nematodes. It is mainly used to study the effects of different chemicals on the perception behavior of nematodes. By conducting this experiment, not only can the neurotoxicity of chemicals be reflected, but also the impact of chemicals on physiological functions regulated by the nervous system, such as nematode feeding behavior and basic motor ability.
Objective: The experiment of detecting the response of nematode to chemicals is also a common method of chemical toxicity testing based on nematode models. In the analysis of worm tendency behavior, manual operations are generally used. Manually processing a large number of worms under a microscope is very time-consuming and labor-intensive. The current quantitative methods for nematode chemotaxis experiments are not only time-consuming and labor-intensive, but also biased in experimental results due to differences in judgment standards among experimenters. The automatic and efficient quantification method for nematode chemotaxis experiments is a very important technical difficulty in the field of nematode experiments.
Methods: Here, we have designed an automatic quantification method for nematode chemotaxis experiments by incorporating image acquisition and processing techniques into the nematode experiment.
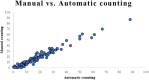
Results: The experimental results show that the Pearson correlation coefficient between manual and automatic counting results is 0.978.
Conclusion: This proves the effectiveness of our method. Applying the automatic measurement method to replace manual counting by the experimenter can improve work efficiency, and reduce errors in human counting operations.
Keywords: C. elegans; automatic quantification; behavior analysis; image processing.
Conflict of interest statement
None to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NemaCount: quantification of nematode chemotaxis behavior in a browser.Invert Neurosci. 2016 Jun;16(2):5. doi: 10.1007/s10158-016-0188-1. Epub 2016 May 21. Invert Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27209025
-
An automatic recognition method of nematode survival rate based on bright field and dark field experimental images.Technol Health Care. 2023;31(S1):199-208. doi: 10.3233/THC-236017. Technol Health Care. 2023. PMID: 37038792 Free PMC article.
-
Fast, automated measurement of nematode swimming (thrashing) without morphometry.BMC Neurosci. 2009 Jul 20;10:84. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-84. BMC Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19619274 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity testing of neurotoxic pesticides in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2014;17(5):284-306. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2014.933722. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2014. PMID: 25205216 Review.
-
Nematode memory: now, where was I?Curr Biol. 2005 May 24;15(10):R374-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.005. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15916936 Review.
References
-
- Wilson IBH, Paschinger K, Cummings RD, Aebi M. Nematoda. 2022.
-
- Ha NM, Tran SH, Shim Y-H, Kang K. Caenorhabditis elegans as a powerful tool in natural product bioactivity research. Appl Biol Chem. 2022; 65: 18.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

