Research Advances in the Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 38755968
- PMCID: PMC11102699
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748241256819
Research Advances in the Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
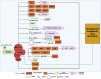
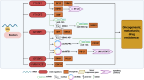
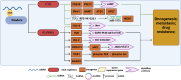
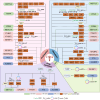
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the most lethal gynecological tumor, characterized by its insidious and frequently recurring metastatic progression. Owing to limited early screening methods, over 70% of OC cases are diagnosed at advanced stages, typically stage III or IV. Recently, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification has emerged as a hotspot of epigenetic research, representing a significant endogenous RNA modification in higher eukaryotes. Numerous studies have reported that m6A-related regulatory factors play pivotal roles in tumor development through diverse mechanisms. Moreover, recent studies have indicated the aberrant expression of multiple regulatory factors in OC. Therefore, this paper comprehensively reviews research advancements concerning m6A in OC, aiming to elucidate the regulatory mechanism of m6A-associated regulators on pivotal aspects, such as proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance, in OC. Furthermore, it discusses the potential of m6A-associated regulators as early diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets, thus contributing to the diagnosis and treatment of OC.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine (m6A); diagnosis; endogenous RNA modification; epigenetic research; metastatic progression; ovarian cancer; prognosis; treatment; tumor microenvironment.
Plain language summary
Ovarian cancer (OC) presents a formidable challenge in the medical field, often detected at advanced stages, necessitating urgent exploration of diagnostic and therapeutic avenues. This review delves into the intricate role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in OC, a dynamic epigenetic process increasingly recognized for its regulatory role in cancer biology. Highlighting recent advancements, the review sheds light on how m6A-related factors influence crucial aspects of OC progression, including tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to treatment. Specifically, m6A methyltransferases, binding proteins, and demethylases exert multifaceted effects on OC progression, influencing the expression of pivotal oncogenes and tumor suppressors. While promising, translating these insights into effective therapies requires further investigation. By comprehensively understanding the influence of m6A on OC, there lies hope for developing improved diagnostic techniques and novel treatment strategies to combat this complex disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N6-Methyladenosine-Related RNA Signature Predicting the Prognosis of Ovarian Cancer.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021;16(3):407-416. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666210615164645. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34137363
-
Gene Signatures and Prognostic Values of m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Control. 2020 Jan-Dec;27(1):1073274820960460. doi: 10.1177/1073274820960460. Cancer Control. 2020. PMID: 32951457 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances of N6-methyladenosine in diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24611. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24611. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35837987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of m6A methylation modification in ovarian cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):663. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02371-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34895230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of RNA modification N6-methyladenosine in human cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Jun 8;19(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01216-3. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32513173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

