Multi - omics analysis for ferroptosis - related genes as prognostic factors in cutaneous melanoma
- PMID: 38755712
- PMCID: PMC11103070
- DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230401
Multi - omics analysis for ferroptosis - related genes as prognostic factors in cutaneous melanoma
Abstract
Objectives: Melanoma is highly malignant and heterogeneous. It is essential to develop a specific prognostic model for improving the patients' survival and treatment strategies. Recent studies have shown that ferroptosis results from the overproduction of lipid peroxidation and is an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death. Despite this, ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) and their clinical significances remain unknown in malignant melanoma. This study aims to assess the role of FRGs in melanoma, with the goal of developing a novel prognostic model that provides new insights into personalized treatment and improvement of therapeutic outcomes for melanoma.
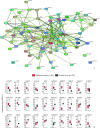
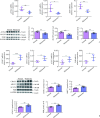
Methods: We systematically characterized the genetic alterations and mRNA expression of 73 FRGs in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM) dataset in this study. The results were validated with real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting. Subsequently, a multi-gene feature model was constructed using the TCGA-SKCM cohort. Melanoma patients were classified into a high-risk group and a low-risk group based on the feature model. As a final step, correlations between ferroptosis-related signatures and immune features, immunotherapy efficacy, or drug response were analyzed.
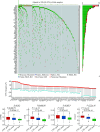
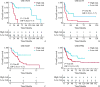
Results: By analyzing melanoma samples from TCGA-SKCM dataset, FRGs exhibited a high frequency of genetic mutations and copy number variations (CNVs), significantly impacting gene expression. Additionally, compared with normal skin tissue, 30 genes with significantly differential expression were identified in melanoma tissues. A prognostic model related to FRGs, constructed using the LASSO Cox regression method, identified 13 FRGs associated with overall survival prognosis in patients and was validated with external datasets. Finally, functional enrichment and immune response analysis further indicated significant differences in immune cell infiltration, mutation burden, and hypoxia status between the high-risk group and the low-risk group, and the model was effective in predicting responses to immunotherapy and drug sensitivity.
Conclusions: This study develops a strong ferroptosis-related prognostic signature model which could put forward new insights into target therapy and immunotherapy for patients with melanoma.
目的: 黑色素瘤具有高度恶性和异质性。开发特定的黑色素瘤预后预测模型对提高患者的生存率和选择治疗策略至关重要。最近,铁死亡已被证明是一种由过度脂质过氧化诱导的铁依赖性程序性细胞死亡形式。然而,铁死亡相关基因(ferroptosis-related genes,FRGs)与黑色素瘤预后的相关性仍不清晰。本研究评估FRGs在黑色素瘤中的作用,开发一种新的预后模型,旨在为黑色素瘤的个性化治疗及疗效改善提供新思路。方法: 首先通过系统地表征癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)-皮肤黑色素瘤(skin cutaneous melanoma,SKCM)中73个FRGs的遗传改变和mRNA表达。同时通过反转录聚合酶链反应和蛋白质印迹法验证筛选的特定靶基因。随后使用TCGA-SKCM队列构建多基因特征模型。根据特征模型将黑色素瘤患者分为高风险和低风险组,对铁死亡相关的特征模型与免疫特征、免疫治疗的疗效或药物反应进行相关分析。结果: 通过分析TCGA-SKCM数据集中的黑色素瘤样本,发现FRGs在基因变异和拷贝数变异方面表现出高频率,这些变化显著影响了基因的表达。此外,与正常皮肤组织相比,在黑色素瘤组织中发现了30个显著差异表达的基因。随后使用LASSO Cox回归方法构建的FRGs相关预后模型成功识别了13个与患者总体生存预后相关的FRGs,并通过外部数据集验证了该模型的有效性。最后,功能富集和免疫响应结果分析进一步表明高风险和低风险组之间存在免疫细胞浸润、突变负担和低氧状态的显著差异,且该模型能有效预测免疫治疗响应和药物敏感性。结论: 本研究建立了一种强预后预测模型,可为黑色素瘤患者的靶向治疗和免疫治疗提供新的方向。.
目的: 黑色素瘤具有高度恶性和异质性。开发特定的黑色素瘤预后预测模型对提高患者的生存率和选择治疗策略至关重要。最近,铁死亡已被证明是一种由过度脂质过氧化诱导的铁依赖性程序性细胞死亡形式。然而,铁死亡相关基因(ferroptosis-related genes,FRGs)与黑色素瘤预后的相关性仍不清晰。本研究评估FRGs在黑色素瘤中的作用,开发一种新的预后模型,旨在为黑色素瘤的个性化治疗及疗效改善提供新思路。
方法: 首先通过系统地表征癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)-皮肤黑色素瘤(skin cutaneous melanoma,SKCM)中73个FRGs的遗传改变和mRNA表达。同时通过反转录聚合酶链反应和蛋白质印迹法验证筛选的特定靶基因。随后使用TCGA-SKCM队列构建多基因特征模型。根据特征模型将黑色素瘤患者分为高风险和低风险组,对铁死亡相关的特征模型与免疫特征、免疫治疗的疗效或药物反应进行相关分析。
结果: 通过分析TCGA-SKCM数据集中的黑色素瘤样本,发现FRGs在基因变异和拷贝数变异方面表现出高频率,这些变化显著影响了基因的表达。此外,与正常皮肤组织相比,在黑色素瘤组织中发现了30个显著差异表达的基因。随后使用LASSO Cox回归方法构建的FRGs相关预后模型成功识别了13个与患者总体生存预后相关的FRGs,并通过外部数据集验证了该模型的有效性。最后,功能富集和免疫响应结果分析进一步表明高风险和低风险组之间存在免疫细胞浸润、突变负担和低氧状态的显著差异,且该模型能有效预测免疫治疗响应和药物敏感性。
结论: 本研究建立了一种强预后预测模型,可为黑色素瘤患者的靶向治疗和免疫治疗提供新的方向。
Keywords: cutaneous melanoma; ferroptosis; immunotherapy; risk score; targeted therapy; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

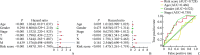
Similar articles
-
Analysis on tumor immune microenvironment and construction of a prognosis model for immune-related skin cutaneous melanoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May 28;48(5):671-681. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230069. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37539569 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Identification and validation of a ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting survival in skin cutaneous melanoma.Cancer Med. 2022 Sep;11(18):3529-3541. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4706. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35373463 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma Molecular Subtypes and Development of Prognostic and Immunotherapy-Related Genetic Characteristics by Ferroptosis Gene Analysis.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 26;2022:2992939. doi: 10.1155/2022/2992939. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9756912. doi: 10.1155/2023/9756912 PMID: 35516454 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Sphingolipid metabolism and regulated cell death in malignant melanoma.Apoptosis. 2024 Dec;29(11-12):1860-1878. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-02002-y. Epub 2024 Jul 28. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 39068623 Review.
-
Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Response to Immunotherapy in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;13(12):2875. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122875. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

