Germline polymorphisms of the NOD2 pathway may predict the effectiveness of radioiodine in differentiated thyroid cancer treatment
- PMID: 38755492
- PMCID: PMC11549118
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-024-02389-0
Germline polymorphisms of the NOD2 pathway may predict the effectiveness of radioiodine in differentiated thyroid cancer treatment
Abstract
Purpose: Differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) presents a complex clinical challenge, especially in patients with distant metastases and resistance to standard treatments. This study aimed to investigate the influence of specific genes and their germline single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) linked to both inflammatory processes and other neoplasms on the clinical and pathological characteristics of DTC, particularly their potential impact on radioiodine (RAI) treatment efficacy.
Methods: This retrospective analysis involved a cohort of 646 patients diagnosed with DTC after thyroidectomy. Study covering 1998-2014, updated in 2023, included 567 women and 79 men (median age: 49; range: 7-83). SNP selection targeted functional significance, while mutational status was assessed by pyrosequencing for comprehensive characterization. Patient genetic profiles were assessed for associations with disease characteristics, RAI response, and cancer pathology.
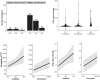
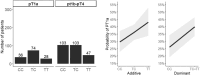
Results: Significant correlations emerged between certain SNPs and DTC features. Notably, the NOD2 c.802 T > C variant (rs2066842) was identified as a marker distinguishing between papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and follicular thyroid cancer (FTC). Moreover, the c.802 T allele was associated with an enhanced response to RAI treatment, indicating a more substantial decrease in posttreatment stimulated thyroglobulin (sTg) concentrations. The NFKB1A allele c.126A (rs696) exhibited connections with lower FTC stages and a reduced probability of multifocality.
Conclusion: This study explored the molecular mechanisms of particular SNPs, highlighting the role of NOD2 in innate immunity and the stress response, and its potential impact on RAI efficacy. This research underscores the clinical promise of SNP analysis and contributes to personalized treatment strategies for DTC, emphasizing the relevance of genetic factors in cancer progression and treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis; Differentiated thyroid cancer; Radioiodine treatment; Single nucleotide polymorphisms; Thyroglobulin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do Molecular Profiles of Primary Versus Metastatic Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Differ?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 25;12:623182. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.623182. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33716974 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing radioiodine therapy long-term outcomes in differentiated thyroid cancer using nomograms.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 7;14(1):23349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72002-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39375397 Free PMC article.
-
Ongoing risk stratification for differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) - stimulated serum thyroglobulin (Tg) before radioiodine (RAI) ablation, the most potent risk factor of cancer recurrence in M0 patients.Endokrynol Pol. 2016;67(1):2-11. doi: 10.5603/EP.2016.0001. Endokrynol Pol. 2016. PMID: 26884109
-
Molecular targets of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in thyroid cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Feb;79:180-196. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.11.013. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33249201 Review.
-
Management of pediatric differentiated thyroid cancer: An overview for the pediatric oncologist.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020 Jun;67(6):e28141. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28141. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32275118 Review.
Cited by
-
Descriptive Analysis of Common Fusion Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Hungary.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10787. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910787. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Houten P, Netea-Maier RT, Smit JW (2023) Differentiated thyroid carcinoma: an update. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 37:101687. 10.1016/j.beem.2022.101687 - PubMed
-
- Jarząb B, Dedecjus M, Lewiński A et al (2022) Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer in adult patients—recommendations of polish scientific societies and the national oncological strategy. 2022 update [diagnostyka i leczenie raka tarczycy u chorych dorosłych - rekomendacje polskich towarzystw naukowych oraz narodowej strategii onkologicznej. aktualizacja na rok 2022]. Endokrynol Pol 73:173–300. 10.5603/EP.a2022.0028 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical