Bacteria-organelle communication in physiology and disease
- PMID: 38748249
- PMCID: PMC11096858
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202310134
Bacteria-organelle communication in physiology and disease
Abstract
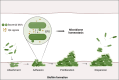
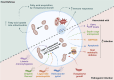
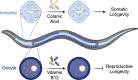
Bacteria, omnipresent in our environment and coexisting within our body, exert dual beneficial and pathogenic influences. These microorganisms engage in intricate interactions with the human body, impacting both human health and disease. Simultaneously, certain organelles within our cells share an evolutionary relationship with bacteria, particularly mitochondria, best known for their energy production role and their dynamic interaction with each other and other organelles. In recent years, communication between bacteria and mitochondria has emerged as a new mechanism for regulating the host's physiology and pathology. In this review, we delve into the dynamic communications between bacteria and host mitochondria, shedding light on their collaborative regulation of host immune response, metabolism, aging, and longevity. Additionally, we discuss bacterial interactions with other organelles, including chloroplasts, lysosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
© 2024 Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Organelle interplay-peroxisome interactions in health and disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020 Jan;43(1):71-89. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12083. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020. PMID: 30864148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic implications of organelle-mitochondria communication.EMBO Rep. 2019 Sep;20(9):e47928. doi: 10.15252/embr.201947928. Epub 2019 Aug 14. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31418169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organelle crosstalk in the kidney.Kidney Int. 2019 Jun;95(6):1318-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.035. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30878214 Review.
-
Independent organelle and organelle-organelle interactions: essential mechanisms for malignant gynecological cancer cell survival.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1393852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393852. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38711526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Organelle Interactions: Unveiling Molecular Mechanisms and Disease Therapies.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2024 Jul;8(7):e2300288. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202300288. Epub 2024 May 8. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38717793 Review.
Cited by
-
EspH utilizes phosphoinositide and Rab binding domains to interact with plasma membrane infection sites and Rab GTPases.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2400575. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2400575. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39312647 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

