TEENA: an integrated web server for transposable element enrichment analysis in various model and non-model organisms
- PMID: 38747349
- PMCID: PMC11223789
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae411
TEENA: an integrated web server for transposable element enrichment analysis in various model and non-model organisms
Abstract
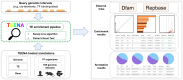
Transposable elements (TEs) are abundant in the genomes of various eukaryote organisms. Increasing evidence suggests that TEs can play crucial regulatory roles-usually by creating cis-elements (e.g. enhancers and promoters) bound by distinct transcription factors (TFs). TE-derived cis-elements have gained unprecedented attentions recently, and one key step toward their understanding is to identify the enriched TEs in distinct genomic intervals (e.g. a set of enhancers or TF binding sites) as candidates for further study. Nevertheless, such analysis remains challenging for researchers unfamiliar with TEs or lack strong bioinformatic skills. Here, we present TEENA (Transposable Element ENrichment Analyzer) to streamline TE enrichment analysis in various organisms. It implements an optimized pipeline, hosts the genome/gene/TE annotations of almost one hundred species, and provides multiple parameters to enable its flexibility. Taking genomic interval data as the only user-supplied file, it can automatically retrieve the corresponding annotations and finish a routine analysis in a couple minutes. Multiple case studies demonstrate that it can produce highly reliable results matching previous knowledge. TEENA can be freely accessed at: https://sun-lab.yzu.edu.cn/TEENA. Due to its easy-to-use design, we expect it to facilitate the studies of the regulatory function of TEs in various model and non-model organisms.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A transposable element annotation pipeline and expression analysis reveal potentially active elements in the microalga Tisochrysis lutea.BMC Genomics. 2018 May 22;19(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4763-1. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29783941 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking transposable element annotation methods for creation of a streamlined, comprehensive pipeline.Genome Biol. 2019 Dec 16;20(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1905-y. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31843001 Free PMC article.
-
McClintock: An Integrated Pipeline for Detecting Transposable Element Insertions in Whole-Genome Shotgun Sequencing Data.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Aug 7;7(8):2763-2778. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.043893. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28637810 Free PMC article.
-
TFs for TEs: the transcription factor repertoire of mammalian transposable elements.Genes Dev. 2021 Jan 1;35(1-2):22-39. doi: 10.1101/gad.344473.120. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33397727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transposable elements as a potent source of diverse cis-regulatory sequences in mammalian genomes.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 30;375(1795):20190347. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0347. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32075564 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals loci linked to human variation in LINE-1- and Alu-copy numbers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 11:2024.09.10.612283. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.10.612283. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314493 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Senft A.D., Macfarlan T.S. Transposable elements shape the evolution of mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021; 22:691–711. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

