LncRNAs, nuclear architecture and the immune response
- PMID: 38738760
- PMCID: PMC11093052
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2350182
LncRNAs, nuclear architecture and the immune response
Abstract
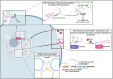
Long noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs) are key regulators of gene expression and can mediate their effects in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Some of the best-characterized lncRNAs are localized within the nucleus, where they modulate the nuclear architecture and influence gene expression. In this review, we discuss the role of lncRNAs in nuclear architecture in the context of their gene regulatory functions in innate immunity. Here, we discuss various approaches to functionally characterize nuclear-localized lncRNAs and the challenges faced in the field.
Keywords: Chromatin; innate immunity; long noncoding RNAs; macrophages; nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
S. C. is a paid consultant for NextRNA Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs as regulators of innate immune cell development and inflammatory gene expression.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Mar;46(3):504-12. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444558. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26820238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs as Organizers of Nuclear Architecture.Sci China Life Sci. 2016 Mar;59(3):236-44. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-5012-y. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Sci China Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26825945 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNA Nuclear Retention.Trends Biochem Sci. 2020 Nov;45(11):947-960. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020. PMID: 32800670 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs: an emerging link between gene regulation and nuclear organization.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Nov;24(11):651-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25441720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulatory functions of nuclear long noncoding RNAs.Trends Genet. 2014 Aug;30(8):348-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Trends Genet. 2014. PMID: 24974018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han D, Fang R, Shi R, et al. LncRNA NKILA knockdown promotes cell viability and represses cell apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis model by regulating miR-140-5p/CLDN2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;559:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.074 - DOI - PubMed
