Herpes Simplex Virus ICP27 Protein Inhibits AIM 2-Dependent Inflammasome Influencing Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Release in Human Pigment Epithelial Cells (hTert-RPE 1)
- PMID: 38731826
- PMCID: PMC11083950
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094608
Herpes Simplex Virus ICP27 Protein Inhibits AIM 2-Dependent Inflammasome Influencing Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Release in Human Pigment Epithelial Cells (hTert-RPE 1)
Abstract
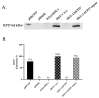
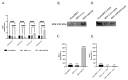
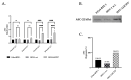
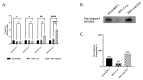
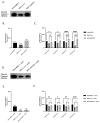
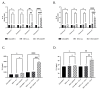
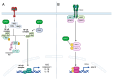
Although Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) has been deeply studied, significant gaps remain in the fundamental understanding of HSV-host interactions: our work focused on studying the Infected Cell Protein 27 (ICP27) as an inhibitor of the Absent-in-melanoma-2 (AIM 2) inflammasome pathway, leading to reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines that influence the activation of a protective innate immune response to infection. To assess the inhibition of the inflammasome by the ICP27, hTert-immortalized Retinal Pigment Epithelial cells (hTert-RPE 1) infected with HSV-1 wild type were compared to HSV-1 lacking functional ICP27 (HSV-1∆ICP27) infected cells. The activation of the inflammasome by HSV-1∆ICP27 was demonstrated by quantifying the gene and protein expression of the inflammasome constituents using real-time PCR and Western blot. The detection of the cleavage of the pro-caspase-1 into the active form was performed by using a bioluminescent assay, while the quantification of interleukins 1β (IL-1β) and 18 (IL-18)released in the supernatant was quantified using an ELISA assay. The data showed that the presence of the ICP27 expressed by HSV-1 induces, in contrast to HSV-1∆ICP27 vector, a significant downregulation of AIM 2 inflammasome constituent proteins and, consequently, the release of pro-inflammatory interleukins into the extracellular environment reducing an effective response in counteracting infection.
Keywords: host–virus interaction; inflammasome; innate immunity; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of cytokine expression by herpes simplex virus in human monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells is dependent on virus replication and is counteracted by ICP27 targeting NF-kappaB and IRF-3.J Gen Virol. 2006 May;87(Pt 5):1099-1108. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81541-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16603509
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Lytic Infection Blocks MicroRNA (miRNA) Biogenesis at the Stage of Nuclear Export of Pre-miRNAs.mBio. 2019 Feb 12;10(1):e02856-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02856-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30755517 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 VP22 Inhibits AIM2-Dependent Inflammasome Activation to Enable Efficient Viral Replication.Cell Host Microbe. 2018 Feb 14;23(2):254-265.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.12.014. Cell Host Microbe. 2018. PMID: 29447697
-
NLRP3, NLRP12, and IFI16 Inflammasomes Induction and Caspase-1 Activation Triggered by Virulent HSV-1 Strains Are Associated With Severe Corneal Inflammatory Herpetic Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 16;10:1631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01631. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31367214 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Immediate Early Protein ICP27 Inhibits IFN-β Production in Mucosal Epithelial Cells by Antagonizing IRF3 Activation.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 26;10:290. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00290. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30863402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mustafa M., Illzam E.M., Muniandy R.K., Sharifah A.M., Nang M.K., Ramesh B. Herpes simplex virus infections, Pathophysiology and Management. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2016;15:85–91. doi: 10.9790/0853-150738591. - DOI
-
- Kumar S.P., Chandy M.L., Shanavas M., Khan S., Suresh K.V. Pathogenesis and life cycle of herpes simplex virus infection-stages of primary, latency and recurrence. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2016;28:350–353. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoms.2016.01.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

