Synthesis and in silico inhibitory action studies of azo-anchored imidazo[4,5-b]indole scaffolds against the COVID-19 main protease (Mpro)
- PMID: 38710746
- PMCID: PMC11074333
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57795-4
Synthesis and in silico inhibitory action studies of azo-anchored imidazo[4,5-b]indole scaffolds against the COVID-19 main protease (Mpro)
Abstract
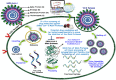
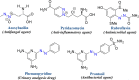
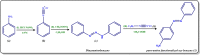
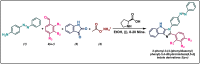
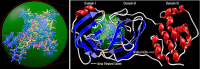
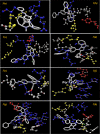
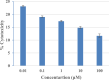
The present work elicits a novel approach to combating COVID-19 by synthesizing a series of azo-anchored 3,4-dihydroimidazo[4,5-b]indole derivatives. The envisaged methodology involves the L-proline-catalyzed condensation of para-amino-functionalized azo benzene, indoline-2,3-dione, and ammonium acetate precursors with pertinent aryl aldehyde derivatives under ultrasonic conditions. The structures of synthesized compounds were corroborated through FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and mass analysis data. Molecular docking studies assessed the inhibitory potential of these compounds against the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2. Remarkably, in silico investigations revealed significant inhibitory action surpassing standard drugs such as Remdesivir, Paxlovid, Molnupiravir, Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), and (N3), an irreversible Michael acceptor inhibitor. Furthermore, the highly active compound was also screened for cytotoxicity activity against HEK-293 cells and exhibited minimal toxicity across a range of concentrations, affirming its favorable safety profile and potential suitability. The pharmacokinetic properties (ADME) of the synthesized compounds have also been deliberated. This study paves the way for in vitro and in vivo testing of these scaffolds in the ongoing battle against SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationship (SAR) and molecular dynamics study of withaferin-A fragment derivatives as potential therapeutic lead against main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2.J Mol Model. 2021 Feb 28;27(3):97. doi: 10.1007/s00894-021-04703-6. J Mol Model. 2021. PMID: 33641023 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of meisoindigo derivatives as noncovalent and orally available Mpro inhibitors: their therapeutic implications in the treatment of COVID-19.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Jul 5;273:116498. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116498. Epub 2024 May 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38762916
-
Search for Non-Protein Protease Inhibitors Constituted with an Indole and Acetylene Core.Molecules. 2021 Jun 23;26(13):3817. doi: 10.3390/molecules26133817. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34201422 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Updated Review on SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteinase (MPro): Protein Structure and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(6):442-460. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666201207095117. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33292134 Review.
Cited by
-
Indole Derivatives: A Versatile Scaffold in Modern Drug Discovery-An Updated Review on Their Multifaceted Therapeutic Applications (2020-2024).Molecules. 2024 Oct 9;29(19):4770. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194770. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed 4 February 2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

