Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs
- PMID: 38707615
- PMCID: PMC11070169
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S447496
Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs
Abstract
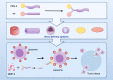
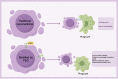
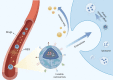
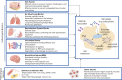
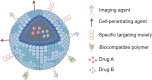
This manuscript offers a comprehensive overview of nanotechnology's impact on the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs, with a focus on BCS Class II and IV drugs. We explore various nanoscale drug delivery systems (NDDSs), including lipid-based, polymer-based, nanoemulsions, nanogels, and inorganic carriers. These systems offer improved drug efficacy, targeting, and reduced side effects. Emphasizing the crucial role of nanoparticle size and surface modifications, the review discusses the advancements in NDDSs for enhanced therapeutic outcomes. Challenges such as production cost and safety are acknowledged, yet the potential of NDDSs in transforming drug delivery methods is highlighted. This contribution underscores the importance of nanotechnology in pharmaceutical engineering, suggesting it as a significant advancement for medical applications and patient care.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; nanotechnology; pharmaceutical engineering; poorly soluble drugs; solubility and bioavailability.
© 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancing Drug Solubility, Bioavailability, and Targeted Therapeutic Applications through Magnetic Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2024 Oct 13;29(20):4854. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204854. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent update of toxicity aspects of nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Apr;161:100-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.02.010. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33639254 Review.
-
Nanocrystal technology in the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: an overview.Curr Drug Deliv. 2011 Jul;8(4):398-406. doi: 10.2174/156720111795767988. Curr Drug Deliv. 2011. PMID: 21453258 Review.
-
Nanonization techniques to overcome poor water-solubility with drugs.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020 Jul;15(7):853-864. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1750591. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32290727 Review.
-
Nanoemulsion as Oral Drug Delivery - A Review.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2020;12(1):4-15. doi: 10.2174/2589977511666191024173508. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31774040 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Evaluation of a Cost-Effective, Carbon-Based, Extended-Release Febuxostat Tablet.Molecules. 2024 Sep 29;29(19):4629. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194629. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407557 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology-driven therapies for neurodegenerative diseases: a comprehensive review.Ther Deliv. 2024;15(12):997-1024. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2401307. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Ther Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39297726 Review.
-
Precious Cargo: The Role of Polymeric Nanoparticles in the Delivery of Covalent Drugs.Molecules. 2024 Oct 19;29(20):4949. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204949. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine for cancer patient-centered care.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 20;5(11):e767. doi: 10.1002/mco2.767. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39434967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baghel S, Cathcart H, O’Reilly NJ, et al. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: a Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J Pharmaceut Sci. 2016;105(9):2527–2544. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2015.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

