Antigen presentation plays positive roles in the regenerative response to cardiac injury in zebrafish
- PMID: 38684665
- PMCID: PMC11058276
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47430-1
Antigen presentation plays positive roles in the regenerative response to cardiac injury in zebrafish
Abstract
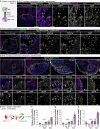
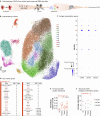
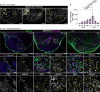
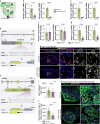
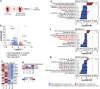
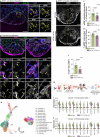
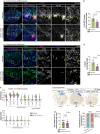
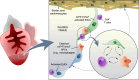
In contrast to adult mammals, adult zebrafish can fully regenerate injured cardiac tissue, and this regeneration process requires an adequate and tightly controlled immune response. However, which components of the immune response are required during regeneration is unclear. Here, we report positive roles for the antigen presentation-adaptive immunity axis during zebrafish cardiac regeneration. We find that following the initial innate immune response, activated endocardial cells (EdCs), as well as immune cells, start expressing antigen presentation genes. We also observe that T helper cells, a.k.a. Cd4+ T cells, lie in close physical proximity to these antigen-presenting EdCs. We targeted Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class II antigen presentation by generating cd74a; cd74b mutants, which display a defective immune response. In these mutants, Cd4+ T cells and activated EdCs fail to efficiently populate the injured tissue and EdC proliferation is significantly decreased. cd74a; cd74b mutants exhibit additional defects in cardiac regeneration including reduced cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation. Notably, Cd74 also becomes activated in neonatal mouse EdCs following cardiac injury. Altogether, these findings point to positive roles for antigen presentation during cardiac regeneration, potentially involving interactions between activated EdCs, classical antigen-presenting cells, and Cd4+ T cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Dynamic Field Theory of Executive Function: Identifying Early Neurocognitive Markers.Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024 Dec;89(3):7-109. doi: 10.1111/mono.12478. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 2024. PMID: 39628288 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
CD74 promotes the formation of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer in mice by inducing the expansion of tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory B cells.PLoS Biol. 2024 Nov 22;22(11):e3002905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002905. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39576827 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich therapies for musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD010071. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010071.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24782334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The innate immune regulator MyD88 dampens fibrosis during zebrafish heart regeneration.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Sep;3(9):1158-1176. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00538-5. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39271818 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

