Multivariate logistic regression analysis of poor prognosis of dermatomyositis and clinical value of ferritin/Kl-6 in predicting prognosis
- PMID: 38682785
- PMCID: PMC11057051
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13701
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of poor prognosis of dermatomyositis and clinical value of ferritin/Kl-6 in predicting prognosis
Abstract
Background: Dermatomyositis (DM) is a rare inflammatory disease. Our research focuses on predicting poor prognosis in DM patients and evaluating the prognostic significance of ferritin and Salivary Sugar Chain Antigen-6 (KL-6) through multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Methods: Between February 2018 and April 2020, 80 DM patients at our hospital were categorized into MDA5 positive (n = 20) and negative (n = 60) groups. We conducted multivariate logistic regression to determine DM's poor prognosis risk factors and evaluate ferritin/KL-6's predictive value for prognosis.
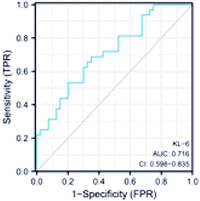
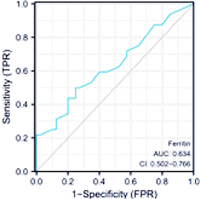
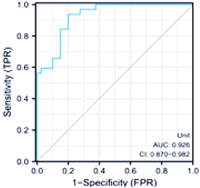
Results: Analysis showed no gender, age, body mass index (BMI), or lifestyle (smoking, drinking) differences, nor in dyspnea, muscle weakness, skin ulcers, and acetylcysteine treatment effects (p > 0.05). Significant differences emerged in arrhythmias, interstitial pneumonia, C-reactive protein, albumin, and lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < 0.05). Before treatment, differences were negligible (p > 0.05), but post-treatment, serum KL-6 and ferritin levels dropped. MDA5 positive patients had elevated serum KL-6 and ferritin levels than survivors (p < 0.05), with a strong correlation to DM. Combined diagnosis using serum KL-6 and ferritin for DM prognosis showed area under curves of 0.716 and 0.634, significantly outperforming single-index diagnoses with an area under curve (AUC) of 0.926 (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Serum KL-6 and ferritin show marked abnormalities in DM, useful as indicators for evaluating polymyositis and DM conditions. However, the study's small sample size is a drawback. Expanding the sample size is essential to monitor serum KL-6 and ferritin changes in DM patients under treatment more closely, aiming to improve clinical assessment and facilitate detailed research.
Keywords: Kl‐6; dermatomyositis; ferritin; multivariate logistic regression analysis.
© 2024 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Evaluating Different Types of Cancer Survivorship Care [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2019 Jul. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2019 Jul. PMID: 39602557 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Huang W, Ren F, Chen D, Wang Z, Tang L. The value of metagenomic next‐generation sequencing in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples of anti‐MDA5‐positive dermatomyositis patients. Rheumatology. 2023;62(3):e36‐e38. - PubMed
-
- He S, Zhou Y, Fan C, et al. Differences in sex‐and age‐associated mortality in patients with anti‐MDA5‐positive dermatomyositis. Modern Rheumatology. 2023;33(5):975‐981. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous