Role of renin-angiotensin system/angiotensin converting enzyme-2 mechanism and enhanced COVID-19 susceptibility in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 38680697
- PMCID: PMC11045416
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i4.606
Role of renin-angiotensin system/angiotensin converting enzyme-2 mechanism and enhanced COVID-19 susceptibility in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
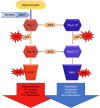
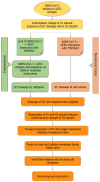
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a disease that caused a global pandemic and is caused by infection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 virus. It has affected over 768 million people worldwide, resulting in approximately 6900000 deaths. High-risk groups, identified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, include individuals with conditions like type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity, chronic lung disease, serious heart conditions, and chronic kidney disease. Research indicates that those with T2DM face a heightened susceptibility to COVID-19 and increased mortality compared to non-diabetic individuals. Examining the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), a vital regulator of blood pressure and pulmonary stability, reveals the significance of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 enzymes. ACE converts angiotensin-I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin-II, while ACE2 counters this by converting angiotensin-II to angiotensin 1-7, a vasodilator. Reduced ACE2 expression, common in diabetes, intensifies RAS activity, contributing to conditions like inflammation and fibrosis. Although ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers can be therapeutically beneficial by increasing ACE2 levels, concerns arise regarding the potential elevation of ACE2 receptors on cell membranes, potentially facilitating COVID-19 entry. This review explored the role of the RAS/ACE2 mechanism in amplifying severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and associated complications in T2DM. Potential treatment strategies, including recombinant human ACE2 therapy, broad-spectrum antiviral drugs, and epigenetic signature detection, are discussed as promising avenues in the battle against this pandemic.
Keywords: Angiotensin-II receptor blockers; Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; COVID-19; Complex diseases; Type 2 diabetes.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare having no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update (Edition 152). 2023. [cited 20 July 2023]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on... .
-
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, Du B, Li LJ, Zeng G, Yuen KY, Chen RC, Tang CL, Wang T, Chen PY, Xiang J, Li SY, Wang JL, Liang ZJ, Peng YX, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu YH, Peng P, Wang JM, Liu JY, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng ZJ, Qiu SQ, Luo J, Ye CJ, Zhu SY, Zhong NS China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1708–1720. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, Pan S, Zou X, Yuan S, Shang Y. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:475–481. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

