Circadian rhythm regulates the function of immune cells and participates in the development of tumors
- PMID: 38678017
- PMCID: PMC11055927
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-01960-1
Circadian rhythm regulates the function of immune cells and participates in the development of tumors
Abstract
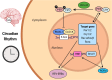
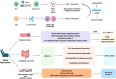
Circadian rhythms are present in almost all cells and play a crucial role in regulating various biological processes. Maintaining a stable circadian rhythm is essential for overall health. Disruption of this rhythm can alter the expression of clock genes and cancer-related genes, and affect many metabolic pathways and factors, thereby affecting the function of the immune system and contributing to the occurrence and progression of tumors. This paper aims to elucidate the regulatory effects of BMAL1, clock and other clock genes on immune cells, and reveal the molecular mechanism of circadian rhythm's involvement in tumor and its microenvironment regulation. A deeper understanding of circadian rhythms has the potential to provide new strategies for the treatment of cancer and other immune-related diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronopharmacological strategies focused on chrono-drug discovery.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Oct;202:72-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31173839 Review.
-
Neutrophil infiltration regulates clock-gene expression to organize daily hepatic metabolism.Elife. 2020 Dec 8;9:e59258. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59258. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33287957 Free PMC article.
-
The Circadian Clock Gene, Bmal1, Regulates Intestinal Stem Cell Signaling and Represses Tumor Initiation.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12(5):1847-1872.e0. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34534703 Free PMC article.
-
miR-34a-dependent overexpression of Per1 decreases cholangiocarcinoma growth.J Hepatol. 2016 Jun;64(6):1295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.024. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26923637 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Effects of Clock and Bmal1 on Circadian Rhythmic TLR Expression.Int Rev Immunol. 2023;42(2):101-112. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1931170. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Int Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 34544330 Review.
Cited by
-
The Influence of Circadian Rhythms on DNA Damage Repair in Skin Photoaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10926. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010926. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Frontier in Cystic Fibrosis Pathophysiology: How and When Clock Genes Can Affect the Inflammatory/Immune Response in a Genetic Disease Model.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 18;46(9):10396-10410. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090618. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoneuroendocrine, circadian and seasonal systems: from photoneuroendocrinology to circadian biology and medicine.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s00441-024-03913-7. Online ahead of print. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 39264444 Review.
-
Circadian rhythms and breast cancer: unraveling the biological clock's role in tumor microenvironment and ageing.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 30;15:1444426. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444426. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39139571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

