The Role of the Placental Enzyme Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Normal and Abnormal Human Pregnancy
- PMID: 38674162
- PMCID: PMC11050494
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084577
The Role of the Placental Enzyme Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Normal and Abnormal Human Pregnancy
Abstract
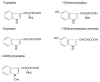
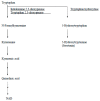
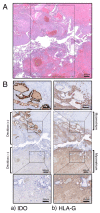
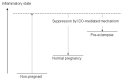
The biologically significant phenomenon that the fetus can survive immune attacks from the mother has been demonstrated in mammals. The survival mechanism depends on the fetus and placenta actively defending themselves against attacks by maternal T cells, achieved through the localized depletion of the amino acid L-tryptophan by an enzyme called indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. These findings were entirely unexpected and pose important questions regarding diseases related to human pregnancy and their prevention during human pregnancy. Specifically, the role of this mechanism, as discovered in mice, in humans remains unknown, as does the extent to which impaired activation of this process contributes to major clinical diseases in humans. We have, thus, elucidated several key aspects of this enzyme expressed in the human placenta both in normal and abnormal human pregnancy. The questions addressed in this brief review are as follows: (1) localization and characteristics of human placental indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenas; (2) overall tryptophan catabolism in human pregnancy and a comparison of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression levels between normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancy; (3) controlling trophoblast invasion by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and its relation to the pathogenesis of placenta accrete spectrum.
Keywords: human pregnancy; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; placenta; placenta accreta spectrum; pre-eclampsia; trophoblast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest in connection with this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of placental indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human pregnancy.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2013 Jul;56(4):209-16. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2013.56.4.209. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24328005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human placental indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: cellular localization and characterization of an enzyme preventing fetal rejection.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Jan 3;1500(1):119-24. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(99)00096-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10564724
-
Impact of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase on the antioxidant system in the placentas of severely pre-eclamptic patients.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2011 Aug;57(4):174-8. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2011.587590. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2011. PMID: 21718232
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in materno-fetal interaction.Curr Drug Metab. 2007 Apr;8(3):205-8. doi: 10.2174/138920007780362491. Curr Drug Metab. 2007. PMID: 17430108 Review.
-
Decreased tryptophan catabolism by placental indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in preeclampsia.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003 Mar;188(3):719-26. doi: 10.1067/mob.2003.156. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003. PMID: 12634647
References
-
- Yoshida R., Hayaishi O. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:188–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

