Heat Shock Response and Heat Shock Proteins: Current Understanding and Future Opportunities in Human Diseases
- PMID: 38673794
- PMCID: PMC11050489
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084209
Heat Shock Response and Heat Shock Proteins: Current Understanding and Future Opportunities in Human Diseases
Abstract
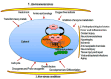
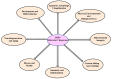
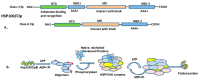
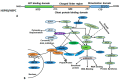
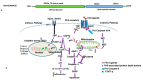
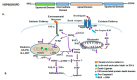
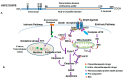
The heat shock response is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that protects cells or organisms from the harmful effects of various stressors such as heat, chemicals toxins, UV radiation, and oxidizing agents. The heat shock response triggers the expression of a specific set of genes and proteins known as heat shock genes/proteins or molecular chaperones, including HSP100, HSP90, HSP70, HSP60, and small HSPs. Heat shock proteins (HSPs) play a crucial role in thermotolerance and aiding in protecting cells from harmful insults of stressors. HSPs are involved in essential cellular functions such as protein folding, eliminating misfolded proteins, apoptosis, and modulating cell signaling. The stress response to various environmental insults has been extensively studied in organisms from prokaryotes to higher organisms. The responses of organisms to various environmental stressors rely on the intensity and threshold of the stress stimuli, which vary among organisms and cellular contexts. Studies on heat shock proteins have primarily focused on HSP70, HSP90, HSP60, small HSPs, and ubiquitin, along with their applications in human biology. The current review highlighted a comprehensive mechanism of heat shock response and explores the function of heat shock proteins in stress management, as well as their potential as therapeutic agents and diagnostic markers for various diseases.
Keywords: apoptosis; heat shock factors; heat shock proteins; human disease; stress response; thermotolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The pleiotropic activity of heat-shock proteins].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009 Oct 27;63:502-21. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009. PMID: 19940329 Review. Polish.
-
Gut myoelectrical activity induces heat shock response in Escherichia coli and Caco-2 cells.Exp Physiol. 2006 Sep;91(5):867-75. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2006.033365. Epub 2006 May 25. Exp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16728456
-
Review: The role of heat shock proteins in chicken: Insights into stress adaptation and health.Res Vet Sci. 2023 Dec;165:105057. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.105057. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Res Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37864906 Review.
-
The role and therapeutic potential of Hsp90, Hsp70, and smaller heat shock proteins in peripheral and central neuropathies.Med Res Rev. 2021 Jan;41(1):202-222. doi: 10.1002/med.21729. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32844464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat shock proteins (chaperones) in fish and shellfish and their potential role in relation to fish health: a review.J Fish Dis. 2010 Oct;33(10):789-801. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2010.01183.x. J Fish Dis. 2010. PMID: 20678104 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Dimethacrylates' Chain Length on Electrical Conductivity and Other Selected Physicochemical Properties of Thermally Sensitive N-isopropylacrylamide Derivatives.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;16(19):2786. doi: 10.3390/polym16192786. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39408495 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of the Search for Neuroprotectors among Bioflavonoids.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 3;17(7):877. doi: 10.3390/ph17070877. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065728 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Chaperonin HSP60: Current Understanding and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5483. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105483. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Substituting Fishmeal with Soy Protein Concentrate Supplemented with Essential Amino Acids in the Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Diet on the Expression of Genes Related to Growth, Stress, Immunity, and Digestive Enzyme.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;14(20):3039. doi: 10.3390/ani14203039. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457969 Free PMC article.
-
Study of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects induced in human fibroblasts by exposure to pulsed and continuous 1.6 GHz radiofrequency.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 31;12:1419525. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1419525. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39145180 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

