High-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging provides new insights into Moyamoya disease
- PMID: 38665292
- PMCID: PMC11043609
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1375645
High-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging provides new insights into Moyamoya disease
Abstract
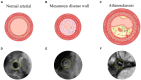
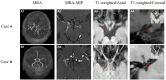
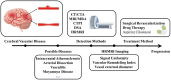
Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a rare condition that affects the blood vessels of the central nervous system. This cerebrovascular disease is characterized by progressive narrowing and blockage of the internal carotid, middle cerebral, and anterior cerebral arteries, which results in the formation of a compensatory fragile vascular network. Currently, digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is considered the gold standard in diagnosing MMD. However, this diagnostic technique is invasive and may not be suitable for all patients. Hence, non-invasive imaging methods such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) are often used. However, these methods may have less reliable diagnostic results. Therefore, High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Vessel Wall Imaging (HR-VWI) has emerged as the most accurate method for observing and analyzing arterial wall structure. It enhances the resolution of arterial walls and enables quantitative and qualitative analysis of plaque, facilitating the identification of atherosclerotic lesions, vascular entrapment, myofibrillar dysplasia, moyamoya vasculopathy, and other related conditions. Consequently, HR-VWI provides a new and more reliable evaluation criterion for diagnosing vascular lesions in patients with Moyamoya disease.
Keywords: Moyamoya disease; cerebral artery occlusion; high-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging; intracranial vessel wall; moyamoya vasculopathy.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Huang, Li, Wu, Zhou, Yin, Zhang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The diagnostic performance of high-resolution magnetic resonance-vessel wall imaging in differentiating atherosclerosis-associated moyamoya vasculopathy from moyamoya disease.Eur Radiol. 2023 Oct;33(10):6918-6926. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09951-z. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37453985
-
Can combined high-resolution vessel wall imaging and multiple post-labeling delay 3D pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling differentiate moyamoya disease from atherosclerotic moyamoya syndrome?Eur J Radiol. 2023 Dec;169:111184. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111184. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Eur J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37931375
-
Quantification of intracranial arterial stenotic degree evaluated by high-resolution vessel wall imaging and time-of-flight MR angiography: reproducibility, and diagnostic agreement with DSA.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):5479-5489. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07719-x. Epub 2021 Feb 14. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33585995
-
Contemporary and emerging magnetic resonance imaging methods for evaluation of moyamoya disease.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Dec 1;47(6):E6. doi: 10.3171/2019.9.FOCUS19616. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31786551 Review.
-
Vessel and Vessel Wall Imaging.Front Neurol Neurosci. 2016;40:109-123. doi: 10.1159/000448308. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27960184 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

