Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: promising strategies to overcoming challenges
- PMID: 38655260
- PMCID: PMC11035781
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1366260
Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: promising strategies to overcoming challenges
Abstract
Resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a significant challenge in the treatment of this disease. The mechanisms of resistance are multifactorial and include molecular target alterations and activation of alternative pathways, tumor heterogeneity and tumor microenvironment change, immune evasion, and immunosuppression. Promising strategies for overcoming resistance include the development of combination therapies, understanding the resistance mechanisms to better use novel drug targets, the identification of biomarkers, the modulation of the tumor microenvironment and so on. Ongoing research into the mechanisms of resistance and the development of new therapeutic approaches hold great promise for improving outcomes for patients with NSCLC. Here, we summarize diverse mechanisms driving resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in NSCLC and the latest potential and promising strategies to overcome the resistance to help patients who suffer from NSCLC.
Keywords: immunotherapy; mechanisms of drug resistance; non-small cell lung cancer; promising strategies; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Xiang, Liu, Wang, Zheng, Meng, Jiang, Yang, Zhang, Zhang, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
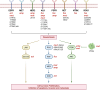
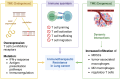
Similar articles
-
Targeting Immunometabolism Mediated by CD73 Pathway in EGFR-Mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A New Hope for Overcoming Immune Resistance.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1479. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01479. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32760402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung cancer: potential targets for immunotherapy.Lancet Respir Med. 2013 Sep;1(7):551-63. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70159-0. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Lancet Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 24461616 Review.
-
Overcoming immunotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) - novel approaches and future outlook.Mol Cancer. 2020 Sep 11;19(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01260-z. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32917214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint blockade as a potential therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016 Oct;16(10):1209-23. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2016.1214265. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27426430 Review.
-
Immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancers: biomarkers for predicting responses and strategies to overcome resistance.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 8;18(1):1082. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4990-5. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30409126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research trends in lung cancer and the tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis of studies published from 2014 to 2023.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 31;14:1428018. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1428018. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39144829 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Patient-Derived Cell-Based Models: Applications and Challenges in Functional Precision Medicine.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;14(9):1142. doi: 10.3390/life14091142. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

