Exertional heat stroke-induced changes in gut microbiota cause cognitive impairment in mice
- PMID: 38654189
- PMCID: PMC11040997
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03276-7
Exertional heat stroke-induced changes in gut microbiota cause cognitive impairment in mice
Abstract
Background: The incidence of exertional heat stroke (EHS) escalates during periods of elevated temperatures, potentially leading to persistent cognitive impairment postrecovery. Currently, effective prophylactic or therapeutic measures against EHS are nonexistent.
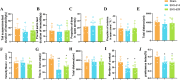
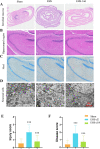
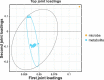
Methods: The selection of days 14 and 23 postinduction for detailed examination was guided by TEM of neuronal cells and HE staining of intestinal villi and the hippocampal regions. Fecal specimens from the ileum and cecum at these designated times were analyzed for changes in gut microbiota and metabolic products. Bioinformatic analyses facilitated the identification of pivotal microbial species and metabolites. The influence of supplementing these identified microorganisms on behavioral outcomes and the expression of functional proteins within the hippocampus was subsequently assessed.
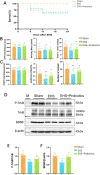
Results: TEM analyses of neurons, coupled with HE staining of intestinal villi and the hippocampal region, indicated substantial recovery in intestinal morphology and neuronal injury on Day 14, indicating this time point for subsequent microbial and metabolomic analyses. Notably, a reduction in the Lactobacillaceae family, particularly Lactobacillus murinus, was observed. Functional annotation of 16S rDNA sequences suggested diminished lipid metabolism and glycan biosynthesis and metabolism in EHS models. Mice receiving this intervention (EHS + probiotics group) exhibited markedly reduced cognitive impairment and increased expression of BDNF/TrKB pathway molecules in the hippocampus during behavioral assessment on Day 28.
Conclusion: Probiotic supplementation, specifically with Lactobacillus spp., appears to mitigate EHS-induced cognitive impairment, potentially through the modulation of the BDNF/TrKB signaling pathway within the hippocampus, illustrating the therapeutic potential of targeting the gut-brain axis.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Exertional heat stroke; Gut microbiota; Gut-brain axis; Probiotic.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probiotic alleviate fluoride-induced memory impairment by reconstructing gut microbiota in mice.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Jun 1;215:112108. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112108. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33799132
-
The Association of Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment and Gut Microbiota and its Corresponding Metabolites.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;73(4):1455-1466. doi: 10.3233/JAD-191066. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 31929168
-
Selenium Nanoparticles-Enriched Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 Prevents Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice Through Modulating Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Oct 13;17:4807-4827. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S374024. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36246933 Free PMC article.
-
Dysbiosis is one of the risk factor for stroke and cognitive impairment and potential target for treatment.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Feb;164:105277. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105277. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33166735 Review.
-
The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of Taxonomic Alterations and Potential Avenues for Interventions.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022 Feb 22;37(3):595-607. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acac008. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2022. PMID: 35202456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus murinus alleviates insulin resistance via promoting L-citrulline synthesis.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Nov 19. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02500-5. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 39560906
References
-
- Gauer R, Meyers BK. Heat-related illnesses. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99:482–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

