In vivo toxicity and antitumor activity of newly green synthesized reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites
- PMID: 38650286
- PMCID: PMC10992821
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-021-00400-7
In vivo toxicity and antitumor activity of newly green synthesized reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites
Abstract
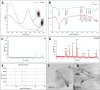
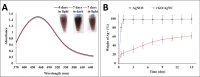
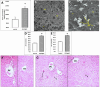
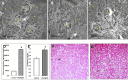
A novel biosynthesis of dual reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites (rGO/AgNC) using the crude metabolite of Escherichia coli D8 (MF06257) strain and sunlight is introduced in this work. Physicochemical analysis of these rGO/AgNC revealed that they are sheet-like structures having spherically shaped silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with an average particle size of 8 to 17 nm, and their absorption peak ranged from 350 to 450 nm. The biosynthesized rGO/AgNC were characterized by UV-vis and FT-IR spectra, X-ray diffraction, Zeta potential and transmission electron microscopy. After the injection of these nanocomposites to mice, their uptake by the kidney and liver has been proven by the ultrastructural observation and estimation of the hepatic and renal silver content. These nanocomposites caused a moderate toxicity for both organs. Changes in the liver and kidney functions and histopathological effects had been observed. The rGO/AgNC revealed a remarkable antitumor effect. They showed a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC) cells in vitro. Treatment of mice bearing EAC tumors intraperitoneally with 10 mg/kg rGO/AgNC showed an antiproliferative effect on EAC cells, reduced ascites volume, and maintained mice survival. The results indicate that this green synergy of silver nanoparticles with reduced graphene oxide may have a promising potential in cancer therapy.
Keywords: Antitumor; Ehrlich ascites carcinoma; In vivo toxicity; Nanocomposites; Reduced graphene oxide; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of green synthesised silver nanoparticles (ST06-AgNPs) using curcumin derivative (ST06) on human cervical cancer cells (HeLa) in vitro and EAC tumor bearing mice models.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 16;14:5257-5270. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S202404. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. Retraction in: Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jul 12;17:3077-3078. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S381653. PMID: 31409988 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Reduced graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: a potential anticancer nanotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Oct 5;10:6257-76. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S92449. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26491296 Free PMC article.
-
Silver nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide: Eco-friendly synthesis, characterization, biological activities and embryo toxicity studies.Environ Res. 2022 Jul;210:112864. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112864. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35149108
-
Facile one pot microbe-mediatedin situsynthesis and antibacterial activity of reduced graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite.Nanotechnology. 2022 Jan 7;33(13). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac4521. Nanotechnology. 2022. PMID: 34933299
-
Combination of graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle nanocomposites and cisplatin enhances apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Sep 5;12:6537-6558. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S125281. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28919753 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anticandidal applications of selenium nanoparticles biosynthesized with Limosilactobacillus fermentum (OR553490).Discov Nano. 2024 Jul 9;19(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s11671-024-04055-z. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 38980559 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Doxorubicin Delivery in Folate-Overexpressed Breast Cancer Cells Using Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres.ACS Omega. 2021 Dec 10;6(50):34532-34545. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04820. eCollection 2021 Dec 21. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34963938 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-liver fibrosis activity of curcumin/chitosan-coated green silver nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 1;12(1):18403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23276-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36319750 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and in vivo toxicological studies of Bi2O3/CuO/GO nanocomposite synthesized via cost effective methods.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 22;12(1):14287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17332-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35995797 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoremediation of tilapia fish culture using iron oxide nanoparticles biosynthesized by Bacillus subtilis and immobilized in a free-floating macroporous cryogel.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Oct 9;20(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04292-5. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39385161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali AA, Madkour M, Sagheer FA, Zaki MI, Abdel Nazeer A. Low-temperature catalytic CO oxidation over non-noble, efficient chromia in reduced graphene oxide and graphene oxide nanocomposites. Catalysts. 2020;10(1):105. doi: 10.3390/catal10010105. - DOI
-
- Alsharaeh E, Alazzam S, Ahmed F, Arshi N, Al-Hindawi M, Sing GK. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as antibacterial agents: A bio-inspired approach. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (english Letters) 2017;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/s40195-016-0485-z. - DOI
-
- Awwad AM, Salem NM, Aqarbeh MM, Abdulaziz FM. Green synthesis, characterization of silver sulfide nanoparticles and antibacterial activity evaluation. Chem Int. 2020;6(1):42–48. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3243157. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

