Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) as Biomarkers in Diagnosis Evaluation of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective, Observational Study
- PMID: 38646605
- PMCID: PMC11027921
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S452444
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) as Biomarkers in Diagnosis Evaluation of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective, Observational Study
Abstract
Purpose: Hierarchical management is advocated in China to effectively manage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients and reduce the incidence and mortality of acute exacerbation of COPD (AE-COPD). However, primary and community hospitals often have limited access to advanced equipment and technology. Complete blood count (CBC), which is commonly used in these hospitals, offers the advantages of being cost-effective and easily accessible. This study aims to evaluate the significance of routine blood indicators in aiding of diagnosing AE-COPD.
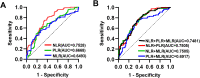
Patients and methods: In this research, we enrolled a total of 112 patients diagnosed with AE-COPD, 92 patients with stable COPD, and a control group comprising 60 healthy individuals. Clinical characteristics, CBC parameters, and serum CRP levels were collected within two hours. To assess the associations between NLR/PLR/MLR and CRP by Spearman correlation test. The diagnostic accuracy of NLR, PLR and MLR in AE-COPD was assessed using Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC) and the area under the curve (AUC). Binary Logistic Regression analysis was conducted for the indicators of NLR, PLR and MLR.
Results: We found that patients with AE-COPD had significantly higher levels of NLR, PLR and MLR in contrast to patients with stable COPD. Additionally, the study revealed a noteworthy correlation between CRP and NLR (rs=0.5319, P<0.001), PLR (rs=0.4424, P<0.001), and MLR (rs=0.4628, P<0.001). By utilizing specific cut-off values, the amalgamation of NLR, PLR and MLR augmented diagnostic sensitivity. Binary logistic regression analysis demonstrated that heightened NLR and MLR act as risk factors for the progression of AE-COPD.
Conclusion: The increasing levels of NLR, PLR and MLR could function as biomarkers, akin to CRP, for diagnosis and assessment of acute exacerbations among COPD patients. Further research is required to validate this concept.
Keywords: AE-COPD; MLR; NLR; PLR; acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; monocyte-lymphocyte ratio; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-lymphocyte ratio.
© 2024 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


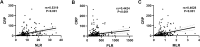
Similar articles
-
Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR), and Eosinophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (ELR) as Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD).Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Feb 23;19:501-518. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S447519. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 38414718 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio for hospital mortality in patients with AECOPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017 Aug 3;12:2285-2290. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S141760. eCollection 2017. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017. PMID: 28814856 Free PMC article.
-
Different biomarker ratios in peripheral blood have limited value in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty: a single-center, retrospective study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 May 13;25(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07499-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38741113 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of platelet and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in COPD patients.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Jan;14(1):111-116. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2019.1675517. Epub 2019 Oct 13. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 31577911 Review.
-
Associations of novel complete blood count-derived inflammatory markers with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 24;316(6):228. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-02994-2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38787437 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Value of Monocyte-To-Lymphocyte Ratio in Differentiating Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis-A Retrospective Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 19;13(20):6249. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206249. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458199 Free PMC article.
-
The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01637-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 38982402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385(9963):117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, et al. China Pulmonary Health Study Group. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2018;391(10131):1706–1717. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30841-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

