Corilagin inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis and fibrillation in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway
- PMID: 38645493
- PMCID: PMC11024412
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.73281.15928
Corilagin inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis and fibrillation in mice through the PI3K-Akt pathway
Abstract
Objectives: Corilagin (Cor) is reported as beiing hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anti-oxidant, while the effect on atrial fibrosis remains unknown. Therefore, we investigated the protective effect of Cor in angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation (AF).
Materials and methods: C57BL/6 mice (male, 8-10 weeks, n = 40) were subcutaneously infused either with saline or Ang II (2.0 mg/kg/day) and Cor (30 mg/kg) intraperitoneally injected 2 hr before Ang II infusion for 4 weeks. Mice were grouped into the control group (n=8), Cor group (n=8), Ang II group (n=8), and Ang II + Cor group (n=8). Morphological, histological, and biochemical examinations were performed. In vivo, transesophageal burst pacing was used to generate AF.
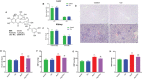
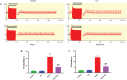
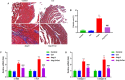
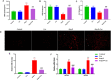
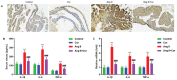
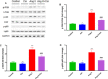
Results: Cor treatment markedly reduced Ang II-induced AF development in mice. Ang II + Cor therapy potentially decreased the atrial fibrotic area. It significantly decreased the increase in smooth muscle alpha-actin (α-SMA), CTGF, Collagen I, and Collagen III expressions brought on by Ang II treatment. Moreover, Ang II + Cor treatment remarkably decreased the malondialdehyde (MDA) content, whereas superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were potentially increased (all, P<0.001). In addition, Ang II + Cor significantly reduced Ang II-induced interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) concentrations in atrial tissues. Furthermore, Cor significantly inhibited Ang II-induced p-PI3K, p-Akt, and NF-κB p-p65 protein expression in atrial tissues.
Conclusion: Our data speculated that Cor could have a protective effect against Ang II-induced atrial fibrosis and AF via down-regulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway.
Keywords: Akt; Angiotensin II; Atrial fibrillation; Atrial fibrosis; Corilagin; PI3K.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest with other people or organizations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corilagin Alleviates Ang II-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Regulating the PTEN/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Dose Response. 2024 Sep 18;22(3):15593258241261198. doi: 10.1177/15593258241261198. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2024. PMID: 39301185 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation by SIRT1/PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway.Heliyon. 2024 May 9;10(10):e30984. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30984. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38803993 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside attenuates atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation vulnerability induced by angiotensin-II through inhibition of LOXL2-TGF-β1-Smad2/3 pathway.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 20;9(11):e21220. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21220. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37920527 Free PMC article.
-
Paeoniflorin Inhibits Atrial Fibrosis and Atrial Fibrillation in Angiotensin II-Infused Mice Through the PI3K-Akt Pathway.Dose Response. 2024 Oct 25;22(4):15593258241277919. doi: 10.1177/15593258241277919. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2024. PMID: 39469468 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin attenuates angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrillation and atrial fibrosis via LOXL2 and TGFβ1/Smad2/3 signaling pathways.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(6):717-724. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68639.14967. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37275755 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Corilagin Alleviates Ang II-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Regulating the PTEN/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Dose Response. 2024 Sep 18;22(3):15593258241261198. doi: 10.1177/15593258241261198. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2024. PMID: 39301185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y, Lv H, Tan R, An X, Niu XH, Liu YJ, et al. Platelets promote Ang II (angiotensin II)-induced atrial fibrillation by releasing TGF-β1 (Transforming Growth Factor-β1) and interacting with fibroblasts. Hypertension. 2020;76:1856–1867. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
