This is a preprint.
Adolescent environmental enrichment induces social resilience and alters neural gene expression in a selectively bred rodent model with anxious phenotype
- PMID: 38645129
- PMCID: PMC11030238
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.03.560702
Adolescent environmental enrichment induces social resilience and alters neural gene expression in a selectively bred rodent model with anxious phenotype
Update in
-
Adolescent environmental enrichment induces social resilience and alters neural gene expression in a selectively bred rodent model with anxious phenotype.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 May 30;31:100651. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100651. eCollection 2024 Jul. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38933284 Free PMC article.
Abstract
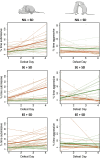
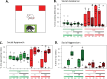
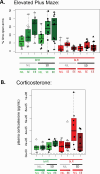
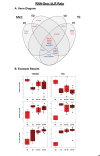
Stress is a major influence on mental health status; the ways that individuals respond to or copes with stressors determine whether they are negatively affected in the future. Stress responses are established by an interplay between genetics, environment, and life experiences. Psychosocial stress is particularly impactful during adolescence, a critical period for the development of mood disorders. In this study we compared two established, selectively-bred Sprague Dawley rat lines, the "internalizing" bred Low Responder (bLR) line versus the "externalizing" bred High Responder (bHR) line, to investigate how genetic temperament and adolescent environment impact future responses to social interactions and psychosocial stress, and how these determinants of stress response interact. Male bLR and bHR rats were exposed to social and environmental enrichment in adolescence prior to experiencing social defeat and were then assessed for social interaction and anxiety-like behavior. Adolescent enrichment caused rats to display more social interaction, as well as nominally less social avoidance, less submission during defeat, and resilience to the effects of social stress on corticosterone, in a manner that seemed more notable in bLRs. For bHRs, enrichment also caused greater aggression during a neutral social encounter and nominally during defeat, and decreased anxiety-like behavior. To explore the neurobiology underlying the development of social resilience in the anxious phenotype bLRs, RNA-seq was conducted on the hippocampus and nucleus accumbens, two brain regions that mediate stress regulation and social behavior. Gene sets previously associated with stress, social behavior, aggression and exploratory activity were enriched with differential expression in both regions, with a particularly large effect on gene sets that regulate social behaviors. Our findings provide further evidence that adolescent enrichment can serve as an inoculating experience against future stressors. The ability to induce social resilience in a usually anxious line of animals by manipulating their environment has translational implications, as it underscores the feasibility of intervention strategies targeted at genetically vulnerable adolescent populations.
Keywords: adolescence; environmental enrichment; genetic environment interactions; social stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adolescent environmental enrichment induces social resilience and alters neural gene expression in a selectively bred rodent model with anxious phenotype.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 May 30;31:100651. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100651. eCollection 2024 Jul. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38933284 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Style Selectively Shapes Amygdalar Development and Social Behavior in Rats Genetically Prone to High Anxiety.Dev Neurosci. 2015;37(3):203-14. doi: 10.1159/000374108. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Dev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25791846 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental underpinnings of differences in rodent novelty-seeking and emotional reactivity.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Sep;34(6):994-1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07811.x. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21864320 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience to Stress: Lessons from Rodents about Nature versus Nurture.Neuroscientist. 2022 Jun;28(3):283-298. doi: 10.1177/1073858421989357. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Neuroscientist. 2022. PMID: 33567987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobiological mechanisms of aggression and stress coping: a comparative study in mouse and rat selection lines.Brain Behav Evol. 2007;70(4):274-85. doi: 10.1159/000105491. Epub 2007 Sep 18. Brain Behav Evol. 2007. PMID: 17914259 Review.
References
-
- Caspi A., et al., Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science, 2003. 301(5631): p. 386–9. - PubMed
-
- Costello E.J., et al., Development and natural history of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry, 2002. 52(6): p. 529–42. - PubMed
-
- Charney D.S., Psychobiological mechanisms of resilience and vulnerability: implications for successful adaptation to extreme stress. Am J Psychiatry, 2004. 161(2): p. 195–216. - PubMed
-
- Southwick S.M., Vythilingam M., and Charney D.S., The psychobiology of depression and resilience to stress: implications for prevention and treatment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol, 2005. 1: p. 255–91. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
