Unveiling the link between lactate metabolism and rheumatoid arthritis through integration of bioinformatics and machine learning
- PMID: 38644410
- PMCID: PMC11033278
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-59907-6
Unveiling the link between lactate metabolism and rheumatoid arthritis through integration of bioinformatics and machine learning
Abstract
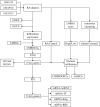
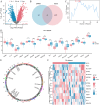
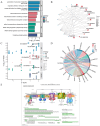
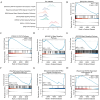
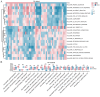
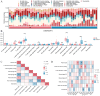
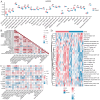
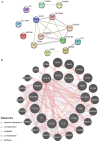
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a persistent autoimmune condition characterized by synovitis and joint damage. Recent findings suggest a potential link to abnormal lactate metabolism. This study aims to identify lactate metabolism-related genes (LMRGs) in RA and investigate their correlation with the molecular mechanisms of RA immunity. Data on the gene expression profiles of RA synovial tissue samples were acquired from the gene expression omnibus (GEO) database. The RA database was acquired by obtaining the common LMRDEGs, and selecting the gene collection through an SVM model. Conducting the functional enrichment analysis, followed by immuno-infiltration analysis and protein-protein interaction networks. The results revealed that as possible markers associated with lactate metabolism in RA, KCNN4 and SLC25A4 may be involved in regulating macrophage function in the immune response to RA, whereas GATA2 is involved in the immune mechanism of DC cells. In conclusion, this study utilized bioinformatics analysis and machine learning to identify biomarkers associated with lactate metabolism in RA and examined their relationship with immune cell infiltration. These findings offer novel perspectives on potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for RA.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Immune infiltration; Lactate metabolism; Machine learning; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of diagnostic genes and drug prediction in metabolic syndrome-associated rheumatoid arthritis by integrated bioinformatics analysis, machine learning, and molecular docking.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1431452. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1431452. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39139563 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and weighted gene co-expression network analysis identify a three-gene signature to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1387311. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1387311. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38711508 Free PMC article.
-
The shared biomarkers and immune landscape in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: Findings based on bioinformatics, machine learning and single-cell analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 7;19(11):e0313344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313344. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39509434 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Disease-Specific Hub Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Tissues by Bioinformatics Analysis.Dis Markers. 2021 May 17;2021:9911184. doi: 10.1155/2021/9911184. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34113405 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic intervention with natural compounds.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jun;100:154048. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154048. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35316725 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

