Progress and hotspot of diet or exercise therapy in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 38628270
- PMCID: PMC11018916
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1326092
Progress and hotspot of diet or exercise therapy in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Introduction: The primary treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is modifying lifestyle through dietary or exercise interventions. In recent decades, it has received increasing attention. However, the lack of bibliometric analysis has posed a challenge for researchers seeking to understand the overall trends in this field.
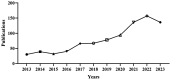
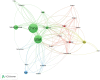
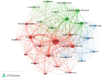
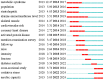
Methods: As of February 3rd, 2024, 876 articles on treating NAFLD through diet or exercise therapy from 2013 to 2023 had been retrieved. Two software tools, VOSviewer and CiteSpace, were utilized to analyze the growth of publications, countries, institutions, authors, journals, citations, and keywords. Additionally, the keywords with strong citation burstiness were identified to determine the changes and future trends of research hotspots in this field.
Results: China had the highest number of articles, followed by the United States and South Korea. Yonsei University and Nutrients were the institutions and journals with the most significant contributions. Professor Younossi Zobair M, from the United States, is the most prolific author in this field. Through analyzing the keywords, three research hotspots were identified: research on the pathogenesis of NAFLD, research on the treatment modalities of NAFLD, and research on the risk factors and diagnosis methods of NAFLD. In recent years, the research emphasis in this field has changed, suggesting that future research will focus on two frontier keywords: "oxidative stress" and "aerobic capacity."
Conclusion: In the past eleven years, the attention in this field was still rising, and the authors, journals, countries and so on had formed a considerable cooperative relationship. There were also many highly influential and productive researchers in this field. It is speculated that new research will continue around "aerobic exercise" and "oxidative stress" in the future.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; diet therapy; exercise therapy; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Copyright © 2024 Shi, Xiong, Song, Rong, Tang, Zhu, Li, Wang, Zhang, You, Ji, Liu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mapping global research trends: Nutrition associations with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - a Scopus bibliometric analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun 28;30(24):3106-3119. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3106. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38983957 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of macrophages associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research from 2005 to 2023.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 7;10(2):e24187. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24187. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293366 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends and hotspots in the links between the bile acids and NAFLD from 2002 to 2022: A bibliometric analysis.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Jan;7(1):e460. doi: 10.1002/edm2.460. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024. PMID: 37941122 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis and visualization of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease from 2012 to 2021.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Oct;23(6):1961-1971. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01023-2. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36795238 Review.
-
Global trends and hotspots of treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A bibliometric and visualization analysis (2010-2023).World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 7;29(37):5339-5360. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5339. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37899789 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping global research trends: Nutrition associations with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - a Scopus bibliometric analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun 28;30(24):3106-3119. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i24.3106. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38983957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association . Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 2018 update. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2018) 26:195–203. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berger S. Kazimierz (Casimir) funk – Pioneer in Vitaminology – 101 anniversary of his discovery – special note. Pol J Food Nutr. (2013) 63:201–5. doi: 10.2478/v10222-012-0100-6 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

