Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Methylation and Long-term Outcomes after Stroke Interacting with Suicidal Ideation
- PMID: 38627077
- PMCID: PMC11024691
- DOI: 10.9758/cpn.23.1115
Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Methylation and Long-term Outcomes after Stroke Interacting with Suicidal Ideation
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the unexplored relationship between BDNF methylation, long-term outcomes, and its interaction with suicidal ideation (SI), which is closely associated with both BDNF expression and stroke outcomes.
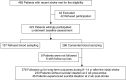
Methods: A total of 278 stroke patients were assessed for BDNF methylation status and SI using suicide-related item in the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale at 2 weeks post-stroke. We investigated the incidence of composite cerebro-cardiovascular events (CCVEs) during an 8-14-year period after the initial stroke as long-term stroke outcome. We conducted Cox regression models adjusted for covariates to evaluate the association between BDNF methylation status and CCVEs, as well as its interaction with post-stroke SI at 2 weeks.
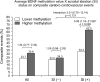
Results: Higher methylation status of CpG 1, 3, and 5, but not the average value, predicted a greater number of composite CCVEs during 8-14 years following the stroke. The associations between a higher methylation status of CpGs 1, 3, 5, and 8, as well as the average BDNF methylation value, and a greater number of composite CCVEs, were prominent in patients who had post-stroke SI at 2 weeks. Notably, a significant interaction between methylation status and SI on composite CCVEs was observed only for CpG 8.
Conclusion: The significant association between BDNF methylation and poor long-term stroke outcomes, particularly amplified in individuals who had post-stroke SI at 2 weeks, suggested that evaluating the biological marker status of BDNF methylation along with assessing SI during the acute phase of stroke can help predict long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Methylation; Outcome assessment; Stroke; Suicidal ideation.
Conflict of interest statement
Jae-Min Kim declares research support in the last 5 years from Janssen and Lundbeck. Sung-Wan Kim declares research support in the last 5 years from Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Allergan and Otsuka. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of SLC6A4 methylation with long-term outcomes after stroke: focus on the interaction with suicidal ideation.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 1;11(1):2710. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81854-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33526821 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Methylation and Suicidal Ideation in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome.Psychiatry Investig. 2018 Oct;15(11):1094-1097. doi: 10.30773/pi.2018.09.20. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Psychiatry Investig. 2018. PMID: 30380818 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction effects of diabetes and brain-derived neurotrophic factor on suicidal ideation in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 22;12(1):6602. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10557-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35459929 Free PMC article.
-
Association between BDNF levels and suicidal behaviour: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 30;4:187. doi: 10.1186/s13643-015-0179-z. Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26718989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as a Clinical Biomarker in Predicting the Development of Post-Stroke Depression: A Review of Evidence.Cureus. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):e15662. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15662. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34141514 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

