Electrocardiographic Effects of Bupropion Toxicity Suggesting Dysfunction of the Gap Junction or Connexin 43
- PMID: 38623136
- PMCID: PMC11018313
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56288
Electrocardiographic Effects of Bupropion Toxicity Suggesting Dysfunction of the Gap Junction or Connexin 43
Abstract
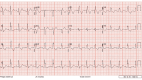
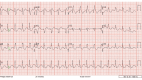
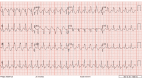
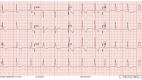
This is a case of a 20-year-old pregnant female presenting EKG abnormalities associated with an overdose of bupropion. These ECG abnormalities are prolongation of the QRS, prolongation of the corrected QT interval (QTc), right axis deviation, and a terminal R wave. The propagation of electricity through the myocardium is dependent on many factors. It is dependent on the flow of sodium from the extracellular to intracellular space, flow of potassium from intracellular to extracellular space, and ultimately the propagation of the signal at the gap junction by Connexin 43 (Cx-43). We postulate that the ECG abnormalities in this case are secondary to bupropion's effect on the potassium rectifier channels (Kir) and or Cx-43 at the gap junction.
Keywords: bupropion; connexin-43; drug overdose and poisoning; ecg; gap junction toxicity.
Copyright © 2024, Bruss et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bupropion overdose: QTc prolongation and its clinical significance.Ann Pharmacother. 2003 Jul-Aug;37(7-8):999-1002. doi: 10.1345/aph.1C481. Ann Pharmacother. 2003. PMID: 12841807 Clinical Trial.
-
Sodium channel blockade with QRS widening after an escitalopram overdose.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013 Sep;29(9):998-1001. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182a314b7. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013. PMID: 24201980
-
QRS widening and QT prolongation under bupropion: a unique cardiac electrophysiological profile.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;26(5):599-608. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2011.00953.x. Epub 2011 May 30. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21623902
-
Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning : cardiovascular toxicity.Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(3):205-14. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524030-00013. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16390222 Review.
-
Antibodies targeting extracellular domain of connexins for studies of hemichannels.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:525-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.021. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23499293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brugada Phenotype Following a Cocaine Overdose.Cureus. 2024 Jul 4;16(7):e63861. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63861. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39099899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Other antidepressants. Schwasinger-Schmidt TE, Macaluso M. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2019;250:325–355. - PubMed
-
- Use of lipid emulsion in the resuscitation of a patient with prolonged cardiovascular collapse after overdose of bupropion and lamotrigine. Sirianni AJ, Osterhoudt KC, Calello DP, et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51:412–415. - PubMed
-
- Sodium bicarbonate treatment for QRS widening in bupropion overdoses. Simpson M, Johnson L, Goldfine C. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2023;61:436–444. - PubMed
-
- Inhibition of G protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels by various antidepressant drugs. Kobayashi T, Washiyama K, Ikeda K. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:1841–1851. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
