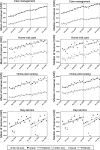
Changes in long-term care insurance revenue among service providers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 38614980
- PMCID: PMC11015625
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-10832-4
Changes in long-term care insurance revenue among service providers during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted peoples' health-related behaviors, especially those of older adults, who have restricted their activities in order to avoid contact with others. Moreover, the pandemic has caused concerns in long-term care insurance (LTCI) providers regarding management and financial issues. This study aimed to examine the changes in revenues among LTCI service providers in Japan during the pandemic and analyze its impact on different types of services.
Methods: In this study, we used anonymized data from "Kaipoke," a management support platform for older adult care operators provided by SMS Co., Ltd. Kaipoke provides management support services to more than 27,400 care service offices nationwide and has been introduced in many home-care support offices. The data used in this study were extracted from care plans created by care managers on the Kaipoke platform. To examine the impact of the pandemic, an interrupted time-series analysis was conducted in which the date of the beginning of the pandemic was set as the prior independent variable.
Results: The participating providers were care management providers (n = 5,767), home-visit care providers (n = 3,506), home-visit nursing providers (n = 971), and adult day care providers (n = 4,650). The results revealed that LTCI revenues decreased significantly for care management providers, home-visit nursing providers, and adult day care providers after the COVID-19 pandemic began. The largest decrease was an average base of USD - 1668.8 in adult day care.
Conclusion: The decrease in revenue among adult day care providers was particularly concerning in terms of the sustainability of their business. This decrease in revenue may have made it difficult to retain personnel, and staff may have needed to be laid off as a result. Although this study has limitations, it may provide useful suggestions for countermeasures in such scenarios, in addition to support conducted measures.
Keywords: COVID-19; Long-term care services; Revenue.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This research was supported by SMS Co., Ltd. and was conducted as a part of the joint research between SMS Co., Ltd. and University of Tsukuba. NT received the fund by SMS Co., Ltd. as the principal investigator of the joint research. MT was a researcher at the University of Tsukuba for joint research with SMS Co., Ltd. in the 2023 financial year (i.e., April 2023 to March 2024). MT and SK were employed by SMS Co., Ltd. TI and XJ had no conflict of interest to be disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Change of Use in Community Services among Disabled Older Adults during COVID-19 in Japan.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jan 28;18(3):1148. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18031148. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33525441 Free PMC article.
-
Older Adults Used Fewer Home Care Services during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Findings from a Secondary Analysis of an Urgent Survey in Japan.Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2021 Dec;25(4):286-293. doi: 10.4235/agmr.21.0108. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34748695 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid mixed-methods evaluation of remote home monitoring models during the COVID-19 pandemic in England.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Jul;11(13):1-151. doi: 10.3310/FVQW4410. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 37800997
-
Considering long-term care insurance for middle-income countries: comparing South Korea with Japan and Germany.Health Policy. 2015 Oct;119(10):1319-29. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Health Policy. 2015. PMID: 26117093 Review.
-
Ensuring the continuation of routine primary care during the COVID-19 pandemic: a review of the international literature.Fam Pract. 2022 Jul 19;39(4):747-761. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab115. Fam Pract. 2022. PMID: 34611708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020. 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical