Biochemical Fractionation of Human α-Synuclein in a Drosophila Model of Synucleinopathies
- PMID: 38612454
- PMCID: PMC11011978
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25073643
Biochemical Fractionation of Human α-Synuclein in a Drosophila Model of Synucleinopathies
Abstract
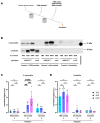
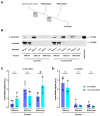
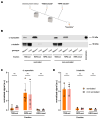
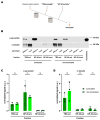
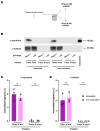
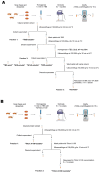
Synucleinopathies are a group of central nervous system pathologies that are characterized by the intracellular accumulation of misfolded and aggregated α-synuclein in proteinaceous depositions known as Lewy Bodies (LBs). The transition of α-synuclein from its physiological to pathological form has been associated with several post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and an increasing degree of insolubility, which also correlate with disease progression in post-mortem specimens from human patients. Neuronal expression of α-synuclein in model organisms, including Drosophila melanogaster, has been a typical approach employed to study its physiological effects. Biochemical analysis of α-synuclein solubility via high-speed ultracentrifugation with buffers of increasing detergent strength offers a potent method for identification of α-synuclein biochemical properties and the associated pathology stage. Unfortunately, the development of a robust and reproducible method for the evaluation of human α-synuclein solubility isolated from Drosophila tissues has remained elusive. Here, we tested different detergents for their ability to solubilize human α-synuclein carrying the pathological mutation A53T from the brains of aged flies. We also assessed the effect of sonication on the solubility of human α-synuclein and optimized a protocol to discriminate the relative amounts of soluble/insoluble human α-synuclein from dopaminergic neurons of the Drosophila brain. Our data established that, using a 5% SDS buffer, the three-step protocol separates cytosolic soluble, detergent-soluble and insoluble proteins in three sequential fractions according to their chemical properties. This protocol shows that sonication breaks down α-synuclein insoluble complexes from the fly brain, making them soluble in the SDS buffer and thus enriching the detergent-soluble fraction of the protocol.
Keywords: Drosophila; Parkinson’s disease; SDS; chemical fractionation; synucleinopathy; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
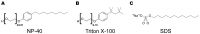
Update of
-
Biochemical fractionation of human α-Synuclein in a Drosophila model of synucleinopathies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 13:2024.02.05.579034. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.05.579034. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3643. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073643 PMID: 38370694 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Biochemical fractionation of human α-Synuclein in a Drosophila model of synucleinopathies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 13:2024.02.05.579034. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.05.579034. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3643. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073643 PMID: 38370694 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Heterogeneity in α-synuclein subtypes and their expression in cortical brain tissue lysates from Lewy body diseases and Alzheimer's disease.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;45(6):597-608. doi: 10.1111/nan.12531. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30422353
-
Multi-platform quantitation of alpha-synuclein human brain proteoforms suggests disease-specific biochemical profiles of synucleinopathies.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Jun 3;10(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01382-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35659116 Free PMC article.
-
The role of phosphorylation in synucleinopathies: focus on Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Aug;9(4):471-81. doi: 10.2174/187152710791556140. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20522010 Review.
-
Pathogenic Impact of α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Its Kinases in α-Synucleinopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 1;23(11):6216. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116216. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tong J., Wong H., Guttman M., Ang L.C., Forno L.S., Shimadzu M., Rajput A.H., Muenter M.D., Kish S.J., Hornykiewicz O., et al. Brain Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation in Multiple System Atrophy, Parkinson’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: A Comparative Investigation. Brain. 2010;133:172–188. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp282. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parra-Rivas L.A., Madhivanan K., Aulston B.D., Wang L., Prakashchand D.D., Boyer N.P., Saia-Cereda V.M., Branes-Guerrero K., Pizzo D.P., Bagchi P., et al. Serine-129 Phosphorylation of α-Synuclein Is an Activity-Dependent Trigger for Physiologic Protein-Protein Interactions and Synaptic Function. Neuron. 2023;111:4006–4023.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.11.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marotta N.P., Ara J., Uemura N., Lougee M.G., Meymand E.S., Zhang B., Petersson E.J., Trojanowski J.Q., Lee V.M.-Y. Alpha-Synuclein from Patient Lewy Bodies Exhibits Distinct Pathological Activity That Can Be Propagated In Vitro. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021;9:188. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01288-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

