Distal colonocytes targeted by C. rodentium recruit T-cell help for barrier defence
- PMID: 38600382
- PMCID: PMC11096101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07288-1
Distal colonocytes targeted by C. rodentium recruit T-cell help for barrier defence
Abstract
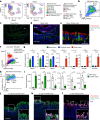
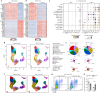
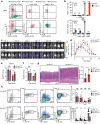
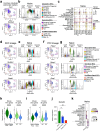
Interleukin 22 (IL-22) has a non-redundant role in immune defence of the intestinal barrier1-3. T cells, but not innate lymphoid cells, have an indispensable role in sustaining the IL-22 signalling that is required for the protection of colonic crypts against invasion during infection by the enteropathogen Citrobacter rodentium4 (Cr). However, the intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) subsets targeted by T cell-derived IL-22, and how T cell-derived IL-22 sustains activation in IECs, remain undefined. Here we identify a subset of absorptive IECs in the mid-distal colon that are specifically targeted by Cr and are differentially responsive to IL-22 signalling. Major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) expression by these colonocytes was required to elicit sustained IL-22 signalling from Cr-specific T cells, which was required to restrain Cr invasion. Our findings explain the basis for the regionalization of the host response to Cr and demonstrate that epithelial cells must elicit MHCII-dependent help from IL-22-producing T cells to orchestrate immune protection in the intestine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
MHC class II antigen presentation by intestinal epithelial cells fine-tunes bacteria-reactive CD4 T-cell responses.Mucosal Immunol. 2024 Jun;17(3):416-430. doi: 10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 19. Mucosal Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37209960
-
MyD88 signaling in dendritic cells and the intestinal epithelium controls immunity against intestinal infection with C. rodentium.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 16;13(5):e1006357. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006357. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28520792 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal epithelium-specific MyD88 signaling impacts host susceptibility to infectious colitis by promoting protective goblet cell and antimicrobial responses.Infect Immun. 2014 Sep;82(9):3753-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02045-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24958710 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T cells drive goblet cell depletion during Citrobacter rodentium infection.Infect Immun. 2013 Dec;81(12):4649-58. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00655-13. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24101690 Free PMC article.
-
A nonredundant role for T cell-derived interleukin 22 in antibacterial defense of colonic crypts.Immunity. 2022 Mar 8;55(3):494-511.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.02.003. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35263568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Type 17 immunity: novel insights into intestinal homeostasis and autoimmune pathogenesis driven by gut-primed T cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Oct 8. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01218-x. Online ahead of print. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39379604 Review.
-
The renaissance of oral tolerance: merging tradition and new insights.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Sep 6. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01077-7. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39242920 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

