Centella asiatica mitigates the detrimental effects of Bisphenol-A (BPA) on pancreatic islets
- PMID: 38580733
- PMCID: PMC10997607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58545-2
Centella asiatica mitigates the detrimental effects of Bisphenol-A (BPA) on pancreatic islets
Abstract
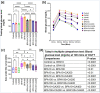
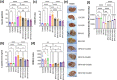
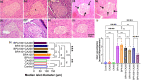
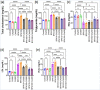
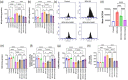
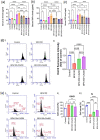
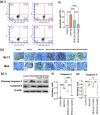
Bisphenol-A (BPA) is widely used in food packaging and household products, leading to daily human exposure and potential health risks including metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Understanding BPA's mechanisms and developing intervention strategies is urgent. Centella asiatica, a traditional herbal medicine containing pentacyclic triterpenoids, shows promise due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, utilized for centuries in Ayurvedic therapy. We investigated the effect of Centella asiatica (CA) ethanol extract on BPA-induced pancreatic islet toxicity in male Swiss albino mice. BPA administration (10 and 100 μg/kg body weight, twice daily) for 21 days caused glucose homeostasis disturbances, insulin resistance, and islet dysfunction, which were partially mitigated by CA supplementation (200 and 400 mg/kg body weight). Additionally, heightened oxidative stress, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), abnormal cell cycle, and increased apoptosis were implicated in the detrimental impact of BPA on the endocrine pancreas which were effectively counteracted by CA supplementation. In summary, CA demonstrated a significant ability to mitigate BPA-induced apoptosis, modulate redox homeostasis, alleviate inflammation, preserve MMP, and regulate the cell cycle. As a result, CA emerged as a potent agent in neutralizing the diabetogenic effects of BPA to a considerable extent.
Keywords: Centella asiatica; Apoptosis; Bisphenol A (BPA); Inflammation; Insulin resistance; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) as a target for Bisphenol-A (BPA)-induced pancreatic islet toxicity and impaired glucose homeostasis: Protective efficacy of ethanol extract of Centella asiatica.Toxicology. 2023 Dec;500:153693. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2023.153693. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Toxicology. 2023. PMID: 38042274
-
Oestrogen receptor β mediates the actions of bisphenol-A on ion channel expression in mouse pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2019 Sep;62(9):1667-1680. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4925-y. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31250031
-
Preventive effects of procyanidin A2 on glucose homeostasis, pancreatic and duodenal homebox 1, and glucose transporter 2 gene expression disturbance induced by bisphenol A in male mice.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;67(2):243-52. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27226184
-
Influence of Bisphenol A on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Oct 6;13(10):989. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13100989. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27782064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dissection of cellular response of pancreatic islet cells to Bisphenol-A (BPA): A comprehensive review.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;201:115068. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115068. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35504317 Review.
Cited by
-
Individual and combined antagonism of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and estrogen receptors (ERs) offers distinct level of protection against Bisphenol A (BPA)-induced pancreatic islet cell toxicity in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 8. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03506-9. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39377923
References
-
- Lin JY, Yin RX. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and type 2 diabetes mellitus in later life. Expo Health. 2023;15:199–229. doi: 10.1007/s12403-022-00486-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

