Multicellular ecotypes shape progression of lung adenocarcinoma from ground-glass opacity toward advanced stages
- PMID: 38554705
- PMCID: PMC11031428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101489
Multicellular ecotypes shape progression of lung adenocarcinoma from ground-glass opacity toward advanced stages
Abstract
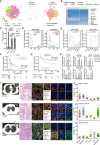
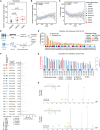
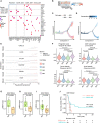
Lung adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that exhibits a wide range of clinical radiological manifestations, from ground-glass opacity (GGO) to pure solid nodules, which vary greatly in terms of their biological characteristics. Our current understanding of this heterogeneity is limited. To address this gap, we analyze 58 lung adenocarcinoma patients via machine learning, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and whole-exome sequencing, and we identify six lung multicellular ecotypes (LMEs) correlating with distinct radiological patterns and cancer cell states. Notably, GGO-associated neoantigens in early-stage cancers are recognized by CD8+ T cells, indicating an immune-active environment, while solid nodules feature an immune-suppressive LME with exhausted CD8+ T cells, driven by specific stromal cells such as CTHCR1+ fibroblasts. This study also highlights EGFR(L858R) neoantigens in GGO samples, suggesting potential CD8+ T cell activation. Our findings offer valuable insights into lung adenocarcinoma heterogeneity, suggesting avenues for targeted therapies in early-stage disease.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
EGFR L858R mutation is associated with lung adenocarcinoma patients with dominant ground-glass opacity.Lung Cancer. 2015 Mar;87(3):272-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.12.016. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25582278
-
Multiomics Analysis Reveals Distinct Immunogenomic Features of Lung Cancer with Ground-Glass Opacity.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Nov 15;204(10):1180-1192. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202101-0119OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34473939 Free PMC article.
-
Discrepancy of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in lung adenocarcinoma presenting as multiple ground-glass opacities.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016 Nov;50(5):909-913. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezw113. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27032467
-
Management of Ground-Glass Opacities in the Lung Cancer Spectrum.Ann Thorac Surg. 2020 Dec;110(6):1796-1804. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.04.094. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32525031 Review.
-
Ground-glass opacity nodules: histopathology, imaging evaluation, and clinical implications.J Thorac Imaging. 2011 May;26(2):106-18. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0b013e3181fbaa64. J Thorac Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21508733 Review.
References
-
- Gettinger S., Horn L., Jackman D., Spigel D., Antonia S., Hellmann M., Powderly J., Heist R., Sequist L.V., Smith D.C., et al. Five-Year Follow-Up of Nivolumab in Previously Treated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the CA209-003 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:1675–1684. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.0412. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fu F., Zhang Y., Wen Z., Zheng D., Gao Z., Han H., Deng L., Wang S., Liu Q., Li Y., et al. Distinct Prognostic Factors in Patients with Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Radiologic Part-Solid or Solid Lesions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019;14:2133–2142. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao J.W., Rizzo S., Ma L.-H., Qiu X.-Y., Warth A., Seki N., Hasegawa M., Zou J.-W., Li Q., Femia M., et al. Pulmonary ground-glass opacity: computed tomography features, histopathology and molecular pathology. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6:68–75. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.01.02. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

