Genetic control of DNA methylation is largely shared across European and East Asian populations
- PMID: 38548728
- PMCID: PMC10978881
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47005-0
Genetic control of DNA methylation is largely shared across European and East Asian populations
Abstract
DNA methylation is an ideal trait to study the extent of the shared genetic control across ancestries, effectively providing hundreds of thousands of model molecular traits with large QTL effect sizes. We investigate cis DNAm QTLs in three European (n = 3701) and two East Asian (n = 2099) cohorts to quantify the similarities and differences in the genetic architecture across populations. We observe 80,394 associated mQTLs (62.2% of DNAm probes with significant mQTL) to be significant in both ancestries, while 28,925 mQTLs (22.4%) are identified in only a single ancestry. mQTL effect sizes are highly conserved across populations, with differences in mQTL discovery likely due to differences in allele frequency of associated variants and differing linkage disequilibrium between causal variants and assayed SNPs. This study highlights the overall similarity of genetic control across ancestries and the value of ancestral diversity in increasing the power to detect associations and enhancing fine mapping resolution.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.E.M. is a scientific advisor to the Epigenetic Clock Development Foundation and Optima Partners. The remaining authors declare no completing interests.
Figures
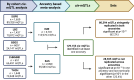
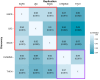
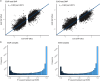

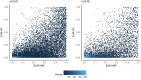
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of cis DNA methylation quantitative trait loci in three Southeast Asian Populations.Hum Mol Genet. 2021 May 12;30(7):603-618. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab038. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 33547791
-
Analysis of blood methylation quantitative trait loci in East Asians reveals ancestry-specific impacts on complex traits.Nat Genet. 2024 May;56(5):846-860. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01494-9. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 38641644
-
Genomic and phenotypic insights from an atlas of genetic effects on DNA methylation.Nat Genet. 2021 Sep;53(9):1311-1321. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00923-x. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 34493871 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping using high-throughput sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1284:257-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2444-8_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25757777 Review.
-
Fine-mapping genetic associations.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Sep 30;29(R1):R81-R88. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa148. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32744321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genes with differential expression across ancestries are enriched in ancestry-specific disease effects likely due to gene-by-environment interactions.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct 3;111(10):2117-2128. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.07.021. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39191255
-
Multiomics Screening Identified CpG Sites and Genes That Mediate the Impact of Exposure to Environmental Chemicals on Cardiometabolic Traits.Epigenomes. 2024 Jul 29;8(3):29. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8030029. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 39189255 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

