Drug Repurposing of Metformin for the Treatment of Haloperidol-Related Behavior Disorders and Oxidative Stress: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 38543297
- PMCID: PMC10974093
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030403
Drug Repurposing of Metformin for the Treatment of Haloperidol-Related Behavior Disorders and Oxidative Stress: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
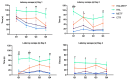
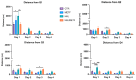
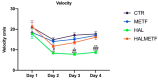
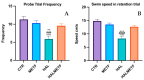
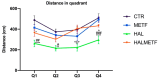
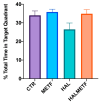
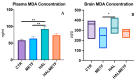
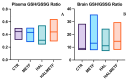
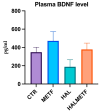
A particular attribute of the brain lies in the ability to learn, acquire information from the environment, and utilize the learned information. Previous research has noted that various factors (e.g., age, stress, anxiety, pathological issues), including antipsychotic medications, affect the brain and memory. The current study aimed to reveal the effects of chronic metformin treatment on the cognitive performance of rats and on commonly measured markers for oxidative stress. Wistar male rats (n = 40) were randomly divided into four groups: CTR (n = 10)-control group, METF (n = 10)-animals receiving metformin 500 mg/kg, HAL (n = 10)-animals receiving haloperidol 2 mg/kg, and HALMETF (n = 10)-animals receiving haloperidol 2 mg/kg and metformin 500 mg/kg. The medication was administered daily by oral gavage for 40 days. Memory and learning were assessed using the Morris Water Maze (MWM) test. At the end of the MWM, the rodents were decapitated under anesthesia, and the brain and blood samples were assayed by liquid chromatography for markers of oxidative stress (malondialdehyde, MDA, reduced/oxidized glutathione ratio, GSH/GSSG). The quantification of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was performed using the conventional sandwich ELISA technique. In the HALMETF group, metformin attenuated the negative effects of haloperidol. Brain and plasma MDA levels increased in the HAL group. Brain and plasma GSH/GSSG ratios and BDNF levels did not reveal any differences between groups. In conclusion, metformin treatment limits the deleterious cognitive effects of haloperidol. The effect on oxidative stress markers may also point toward an antioxidant-like effect of metformin, but this needs further tests for confirmation.
Keywords: cognition; glutathione; malondialdehyde; metformin; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoselenium improved learning, memory, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor and attenuated nitric oxide, and oxidative stress in the brain of juvenile hypothyroid rats.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Dec;37(8):2719-2733. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01073-7. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 36083424
-
Protective role of metformin against methamphetamine induced anxiety, depression, cognition impairment and neurodegeneration in rat: The role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways.Neurotoxicology. 2019 May;72:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30742852
-
Metformin Eased Cognitive Impairment Induced by Chronic L-methionine Administration: Potential Role of Oxidative Stress.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014 Mar;12(2):186-92. doi: 10.2174/1570159X11666131120223201. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24669211 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of metformin on learning and memory behaviors and brain mitochondrial functions in high fat diet induced insulin resistant rats.Life Sci. 2012 Oct 5;91(11-12):409-414. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.08.017. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22925597
-
Neuronal Nitric Oxide Inhibitor 7-Nitroindazole Improved Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Attenuated Brain Tissues Oxidative Damage and Learning and Memory Impairments of Hypothyroid Juvenile Rats.Neurochem Res. 2020 Nov;45(11):2775-2785. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03128-6. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32930947
Cited by
-
Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 19;16(14):2326. doi: 10.3390/nu16142326. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sluggett J.K., Koponen M., Bell J.S., Taipale H., Tanskanen A., Tiihonen J., Uusitupa M., Tolppanen A.M., Hartikainen S. Metformin and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease among Community-Dwelling People with Diabetes: A National Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020;105:dgz234. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgz234. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ha J., Choi D.W., Kim K.J., Cho S.Y., Kim H., Kim K.Y., Koh Y., Nam C.M., Kim E. Association of metformin use with Alzheimer’s disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A population-based nested case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:24069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03406-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

