Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes
- PMID: 38542535
- PMCID: PMC10971636
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063562
Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes
Abstract
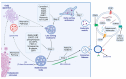
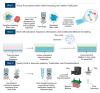
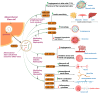
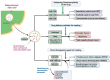
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles of endosomal origin, ranging from 30 to 150 nm in diameter, that mediate intercellular transfer of various biomolecules, such as proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and metabolites. They modulate the functions of recipient cells and participate in diverse physiological and pathological processes, such as immune responses, cell-cell communication, carcinogenesis, and viral infection. Stem cells (SCs) are pluripotent or multipotent cells that can differentiate into various cell types. SCs can also secrete exosomes, which exhibit remarkable therapeutic potential for various diseases, especially in the field of regenerative medicine. For example, exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) contain proteins, lipids, and miRNAs that can ameliorate endocrine disorders, such as diabetes and cancer. Exosomes from SCs (sc-exos) may offer similar advantages as SCs, but with reduced risks and challenges. Sc-exos have lower tumorigenicity, immunogenicity, and infectivity. They can also deliver drugs more efficiently and penetrate deeper into tissues. In this review, we provide an overview of the recent advances in sc-exos and their therapeutic applications in various diseases, such as diabetes and cancer. We also elucidate how the biological effects of sc-exos depend on their molecular composition. We also address the current challenges and future directions of using sc-exos.
Keywords: diabetic microvascular complications; exosomes; microRNAs; precision medicine; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Insight into the Therapeutic Effects of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Respiratory Diseases and the Potential for Pulmonary Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 3;23(11):6273. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116273. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis, Composition and Potential Therapeutic Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosomes in Various Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun 14;18:3177-3210. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S407029. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37337578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contents of exosomes derived from adipose tissue and their regulation on inflammation, tumors, and diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 16;15:1374715. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1374715. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39220365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering exosomes derived from subcutaneous fat MSCs specially promote cartilage repair as miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles in Osteoarthritis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Sep 22;21(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02086-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37736726 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine.World J Stem Cells. 2020 Aug 26;12(8):814-840. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.814. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32952861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stem Cell-Based Acellular Therapy: Insight into Biogenesis, Bioengineering and Therapeutic Applications of Exosomes.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 3;14(7):792. doi: 10.3390/biom14070792. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in joint diseases: Therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jul 27;48:53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.07.005. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 39170747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Stem Cell Therapy for Critical-Sized Segmental Bone Defects: Current Trends and Challenges on the Path to Clinical Translation.J Funct Biomater. 2024 May 27;15(6):145. doi: 10.3390/jfb15060145. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38921519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell-derived exosomes for ischemic stroke: a conventional and network meta-analysis based on animal models.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1481617. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1481617. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39508049 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells in translational challenges.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 13;9(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01936-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39271680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

