Hepatitis B in Pediatric Population: Observational Retrospective Study in Romania
- PMID: 38541675
- PMCID: PMC10970939
- DOI: 10.3390/life14030348
Hepatitis B in Pediatric Population: Observational Retrospective Study in Romania
Erratum in
-
Correction: Păcurar et al. Hepatitis B in Pediatric Population: Observational Retrospective Study in Romania. Life 2024, 14, 348.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;14(9):1075. doi: 10.3390/life14091075. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337994 Free PMC article.
Abstract
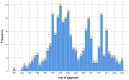
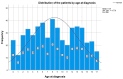
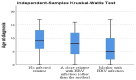
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a frequent cause of chronic hepatitis worldwide, with an estimated 5.6 million children under 5 years being infected. In Romania, there are no available epidemiology reports on large cohorts in children. We aimed to assess the profile of pediatric chronic HBV infection in southern Romania. We conducted an observational retrospective study on 506 HBV-infected children. Based on alaninaminotransferase (ALT), HBV serology and viremia, we identified four states of the disease. We correlated age, gender, household HBV infection, coinfection with other viruses and laboratory parameters. Most patients were in a positive HBV envelope antigen (HBeAg) immune-active state (65.4%). Age at diagnosis was significantly lower for those with household infection (p < 0.05). ALT values were not significantly different between positive or negative HBeAg patients in the immune-active state (p = 0.780). ALT values were higher in patients with hepatitis D virus (HDV)-associated infection (p < 0.001). Children with a household HBV infection had a high viraemia more frequently when compared to those with no infected relative (79.3% vs. 67.4%) (p < 0.001), but the ALT values were not significantly different (p = 0.21). Most of the patients are in an immune-active state (high ALT, high viremia). The percentages of HBV- and HDV-associated infections are high, but lower than the reported prevalence in Romania in the general population.
Keywords: ALT; AST; HBV; HCV; HDV; hepatitis B; transaminases; viraemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and clinical course of hepatitis delta infection in Greece: a 13-year prospective study.J Hepatol. 2013 Nov;59(5):949-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.005. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23850875
-
A cross-sectional epidemiological study of HBV, HCV, HDV and HEV prevalence in the SubCarpathian and South-Eastern regions of Romania.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010 Mar;19(1):43-8. doi: 10.1007/s11749-009-0177-3. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010. PMID: 20361074
-
Epidemiology of hepatitis D in patients infected with hepatitis B virus in bucharest: a cross-sectional study.J Med Virol. 2013 May;85(5):769-74. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23524. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Med Virol. 2013. PMID: 23408537
-
Epidemiology of hepatitis D virus infection in Europe: Is it vanishing?J Viral Hepat. 2024 Feb;31(2):120-128. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13899. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Viral Hepat. 2024. PMID: 37964693 Review.
-
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: case selection and duration of therapy.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002 Apr;17(4):409-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02767.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 11982721 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Păcurar et al. Hepatitis B in Pediatric Population: Observational Retrospective Study in Romania. Life 2024, 14, 348.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;14(9):1075. doi: 10.3390/life14091075. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337994 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

